Apple Inc., the technology giant known for its innovative products and sleek designs, has dominated the industry for decades. However, behind its success lies a series of governance challenges as demonstrated by our Apple sentiment data which shows a steady decline in governance perception. Apple’s governance issues have tested the company’s ability to maintain its position in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. This article will delve into the key governance issues faced by Apple, analyzing its board of directors, CEO succession planning, and the impact of these challenges on its reputation and brand. Furthermore, it will compare Apple’s governance issues practices with industry peers, explore the steps taken by the company to address governance concerns, and discuss the role of shareholders in influencing Apple’s governance.
Apple’s governance issues and Apple board members
Apple board of directors
Apple’s board of directors plays a crucial role in shaping the company’s governance structure and strategic direction. The board of directors at Apple consists of experienced professionals from diverse backgrounds, bringing a wealth of expertise to Apple Inc. Recently, the board of Apple has undergone significant changes, reflecting the company’s commitment to diversity and fresh perspectives. As of the latest update, the Apple Inc. board members include Tim Cook, who serves as both Chief Executive Officer and a board member, along with other distinguished individuals from various industries. Notable members include Ronald Sugar, who joined Apple’s board in 2010 and serves as the chairman of the board. The board also includes former executives who have held positions such as vice president in other major corporations, contributing valuable insights to Apple’s corporate strategy. The board of directors of Apple is responsible for overseeing major corporate decisions, risk management, and ensuring the company’s long-term success.
Board of Apple and diversity concerns
Historically, one of the key governance issues faced by Apple was the composition of its board of directors with a lack of diversity, gender and expertise. However just a week before writing this, Apple announced a massive board shake up as longtime board members step down. The retirement of Al Gore and James Bell and the appointment of Wanda Austin mean there will be an equal number of men and women in the group’s executive committee. This is a huge milestone for the tech giant and the with the recent shake-up, the Apple Inc. directors now reflect a more balanced gender representation, addressing previous concerns about board diversity. This evolution in the composition of Apple’s board of directors demonstrates the company’s responsiveness to governance issues and its dedication to maintaining strong corporate leadership.
Succession planning
Another governance issue that Apple has faced is its CEO succession planning. Steve Jobs, the co-founder and visionary behind Apple’s success, passed away in 2011, leaving a void in leadership. Tim Cook, who had been serving as Apple’s Chief Operating Officer, stepped in as CEO. While Cook has successfully guided Apple through several product launches and business challenges, some investors and analysts have raised questions about the company’s long-term leadership succession plan.
However, in a recent interview with Dua Lipa on her podcast, At Your Service, Apple CEO Tim Cook discussed something that he and Apple almost never address: the succession plan they have in place regarding the company’s leadership. Cook wouldn’t comment on who is in line to replace him at the helm. But he did say that he “really want[s] the [next CEO] to come from within Apple,” and he views part of his role as making sure the board has several internal candidates to choose from.
Executive compensation
High pay packages for executives and a lack of transparency in compensation calculations could indicate potential conflicts of interest, misalignment with shareholder interests, and the need for improved oversight. This aspect of governance is crucial in ensuring that executive compensation aligns with the company’s performance and shareholders’ expectations. Enhancing transparency and accountability in this area contributes to fostering trust among stakeholders and reinforces principles of good corporate governance within Apple.
Labour practices
While primarily ethical and social concerns, the issues surrounding working conditions in supplier factories and unionization efforts indirectly connect to governance. These highlight potential gaps in due diligence, oversight, and responsible sourcing practices within Apple’s supply chain, which fall under the purview of good governance. By addressing these labour-related challenges, Apple has an opportunity to strengthen its commitment to ethical conduct and responsible corporate citizenship, contributing to enhanced governance practices.
App store policies
Antitrust concerns and criticisms of high App Store fees relate to the power dynamics and control Apple exercises within its ecosystem, impacting competition and fair market practices. This goes beyond just business decisions and raises questions about governance, ethical conduct, and responsible use of market power. The company’s policies, in the context of the App Store, underscore the importance of ethical considerations and the responsible exercise of authority in shaping a fair and competitive digital marketplace.
Impact of the board of directors of Apple and governance issues
The impact of Apple’s governance issues on its reputation and brand encompasses both negative and positive dimensions. On the negative side, criticisms surrounding board diversity, executive compensation, and labour practices can erode trust and transparency, raising doubts about Apple’s commitment to ethics and social responsibility. This may result in negative media coverage, public scrutiny, investor concerns, and potential financial consequences, as well as affect employee morale, recruitment efforts, and customer loyalty.
However, there are potential positive impacts arising from these challenges. The increased awareness and dialogue around issues such as board diversity and labour rights can drive positive change within Apple and the broader industry. These challenges present an opportunity for Apple to initiate improvements and reforms, reinforcing its ethical practices and long-term sustainability. Engaging with stakeholders and openly addressing criticisms can help rebuild trust and demonstrate a commitment to transparency and accountability.
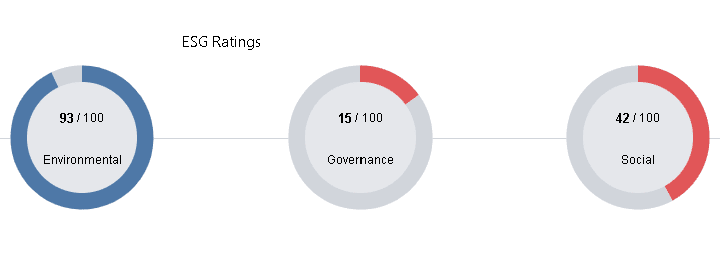
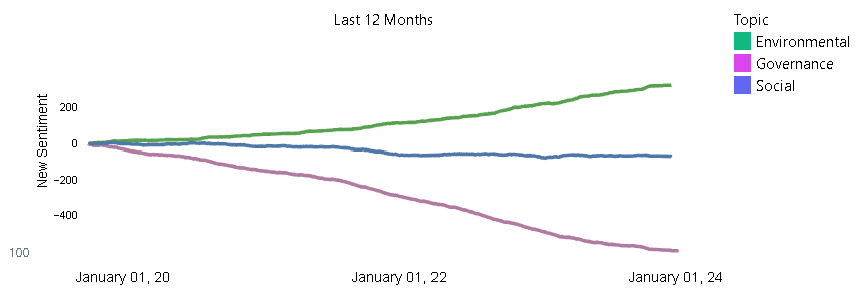
Comparison of Apple’s governance issues with industry peers
When compared to its industry peers, Apple’s governance practices are both commendable and concerning. On one hand, Apple has taken steps to increase board diversity by appointing more women to its board of directors. However, the company still lags behind some of its competitors in terms of gender representation. Additionally, while Apple has a rigorous CEO succession planning process in place, it has been criticized for not being transparent enough about its plans. In comparison, some of its competitors have adopted more open and transparent approaches to CEO succession planning. Here’s a breakdown of key areas:
Board diversity
Apple: Catching up in terms of board diversity.
Peers: Microsoft, Alphabet (Google’s parent company), and IBM have made earlier strides in diverse leadership, boasting boards with higher representation of women and minorities prior to Apple’s recent board shakeup.
Executive compensation
Apple: Tim Cook’s high pay package generates criticism, especially amid stock price decline. Lack of transparency in compensation calculations fuels concerns about accountability.
Peers: Some peers like Microsoft and Alphabet tie executive pay more closely to company performance, and provide clearer disclosure, reducing potential for criticism.
Transparency and accountability
Apple: Limited transparency surrounding certain decision-making processes and internal policies can raise questions about accountability and responsiveness to stakeholders.
Peers: Some peers like Google and Facebook have strengthened transparency measures by publishing detailed sustainability reports and engaging in open communication with stakeholders.
Social responsibility and ethical practices
Apple: Labour practices in supplier factories and concerns about cobalt mining raise ethical concerns about Apple’s supply chain. App Store policies facing antitrust scrutiny.
Peers: Microsoft and IBM have made significant commitments to responsible sourcing and ethical labour practices. Alphabet faces similar antitrust concerns regarding the Play Store.
Overall
Apple: Strengths lie in innovative products and strong brand loyalty, but governance practices lag behind some peers in areas like diversity, transparency, and ethical practices.
Peers: While also facing their own challenges, some peers demonstrate more actively in addressing concerns regarding board diversity, executive compensation, and social responsibility.
Steps taken to address Apple’s governance issues
While Apple faces criticism for its governance practices, it’s important to acknowledge the steps it has taken to address these concerns:
Board diversity
Increased female representation: In 2023, Apple added two women to its board, bringing the total female representation to one out of nine members. While critics argue this progress is slow, it marks a move towards increased diversity.
Focus on skills and experience: Apple emphasizes diverse expertise and experience when selecting board members, regardless of gender or race. This approach aims to ensure a qualified board while acknowledging concerns about representation.
Executive compensation
Linking pay to performance: Apple has partially linked Tim Cook’s pay to Apple’s stock performance, addressing concerns about excessive compensation regardless of company performance.
Increased transparency: Apple publishes detailed compensation reports outlining executive pay packages, although some still call for further breakdown and justification of specific figures.
Transparency and accountability
Enhanced sustainability reporting: Apple publishes comprehensive sustainability reports outlining its environmental and social impacts, addressing calls for increased transparency.
Stakeholder engagement: Apple holds shareholder meetings and engages with various stakeholders on critical issues, although critics argue for more regular and open communication.
Social responsibility and ethical practices:
Supplier responsibility initiatives: Apple implements supplier codes of conduct and conducts audits to address concerns about labor practices in its supply chain. While challenges remain, Apple demonstrates active efforts in this area.
App Store policy adjustments: Apple has made some concessions to developers concerning App Store policies, such as reducing the commission for smaller businesses. However, antitrust concerns persist.
Apple’s efforts to address governance concerns are ongoing and face continued scrutiny. While some progress has been made in areas like board diversity, executive compensation, and transparency, critics argue that the pace is slow and the actions don’t fully address underlying issues. Apple’s future success in improving its governance practices will depend on its continued commitment to addressing these concerns in a substantial and effective manner.
The role of shareholders in influencing Apple’s governance
Shareholders play a crucial role in influencing Apple’s governance. As owners of the company, shareholders have the power to vote on important governance matters, such as the election of directors and executive compensation. In recent years, shareholder activism has increased, with investors using their voting power to push for changes in board composition and governance practices. This demonstrates the growing importance of shareholder engagement in shaping corporate governance.
The future of Apple’s governance in a rapidly evolving technological landscape
In conclusion, Apple’s governance issues have tested the company’s ability to maintain its position in a rapidly evolving technological landscape. While the company has made strides to address these concerns, there is still work to be done. Enhancing board diversity, improving CEO succession planning, and increasing transparency are all critical steps for Apple to ensure effective governance. As the company continues to innovate and shape the future of technology, its governance practices will play a crucial role in maintaining its reputation and brand.
Unlock deeper insights into Apple’s governance
Curious to explore granular data on Apple’s governance issues? Request to see our ESG datasets and find out about our real-time company ESG alerts to make informed decisions using our advanced news sentiment analysis.