In an era of growing environmental consciousness, investors are increasingly seeking companies committed to sustainability and ethical practices. Citigroup, the global banking giant, has recently garnered attention with its ESG rating. But what exactly does the Citigroup ESG rating signify? And how does it influence both the bank’s operations and the broader environment? This article delves into the intricacies of Citigroup’s ESG rating, exploring its implications for investors and its potential impact on our planet. Whether you’re a seasoned investor seeking informed decision-making or an individual passionate about the future of our world, this compelling read unveils the significance of this crucial subject.
Understanding ESG ratings and their importance for investors
Before we dive into our Citigroup ESG rating, let’s first understand what an ESG rating is and why it’s important for investors. ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance, and refers to the three key factors that are used to evaluate a company’s sustainability and ethical practices.
Environmental factors are concerned with the impact a company has on the environment, including its carbon footprint, waste management, and resource conservation efforts. Social factors are concerned with the impact a company has on society, including its labour practices, diversity and inclusion policies, and community involvement. Governance factors are concerned with the way a company is managed and governed, including its board diversity, executive compensation, and transparency.
ESG ratings are used by investors to evaluate the sustainability and ethical practices of companies they are considering investing in. By considering these factors, investors can make more informed decisions about where to put their money, and can choose to support companies that align with their values and priorities.
Citigroup ESG rating – What it means for sustainability
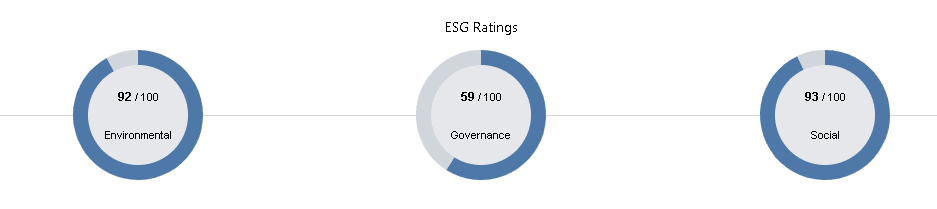
The Citigroup ESG rating is strong across the board. Their environmental rating stands at 92, their social rating at 93 and finally governance at 59. This rating places Citigroup in the top 21% of banks globally, and reflects the bank’s strong performance across a range of ESG factors.
Citigroup’s high score in the environmental category, reflects the bank’s efforts to reduce its carbon footprint and manage its resource use. Citigroup has set ambitious goals to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions and increase its use of renewable energy sources, and has been recognized by a number of organizations for its sustainability efforts.
Citigroup also scored well in the social category, reflecting the bank’s efforts to promote diversity and inclusion, and its support for community development initiatives. Citigroup has implemented a number of programs and policies aimed at increasing diversity in its workforce, and has provided funding and support for a range of community development initiatives around the world.
Finally, Citigroup scored well (though not as highly) in the category, reflecting the bank’s efforts to improve its corporate governance practices in recent years. Citigroup has implemented a number of governance reforms, including changes to its executive compensation structure and improvements to its board diversity.
Overall, the Citigroup ESG rating reflects the bank’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices, and provides investors with valuable information about the bank’s performance in these areas.
Citigroup’s ESG rating – How it compares to other banks
While Citigroup’s ESG rating of A- is certainly impressive, it’s important to consider how it compares to other banks.
When we compare Citigroup’s ESG rating to those of other banks, we see that it is in the top 21% globally. However, it is important to note that there are still many banks that score higher than Citigroup in terms of their sustainability and ethical practices. See how Citibank compares to their competitors below:
– Standard Chartered ESG report
The impact of ESG ratings on investment decisions
ESG ratings can have a significant impact on investment decisions. By providing investors with information about a company’s sustainability and ethical practices, ESG ratings can help investors make more informed decisions about where to put their money.
For example, investors who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices may choose to invest in companies with high ESG ratings, while avoiding companies with low ratings. In this way, ESG ratings can serve as a powerful tool for promoting sustainability and ethical practices among companies.
ESG ratings can also affect a company’s access to capital. Investors who prioritize sustainability and ethical practices may be more likely to invest in companies with high ESG ratings, providing these companies with greater access to capital. On the other hand, companies with low ESG ratings may struggle to attract investment, limiting their ability to grow and expand.
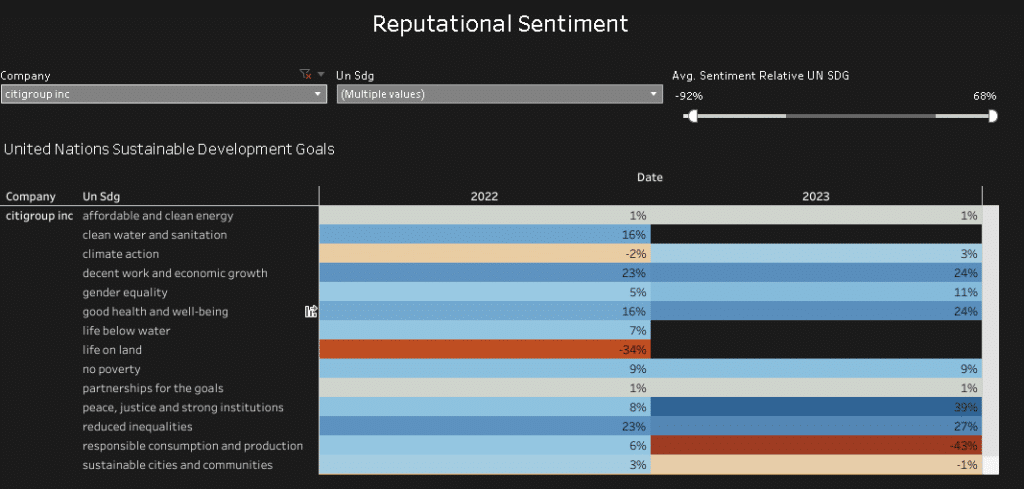
Evaluating Citigroup’s sustainability efforts beyond their ESG rating
While the Citigroup’ ESG rating is certainly an important factor to consider when evaluating the bank’s sustainability and ethical practices, it is important to look beyond the rating to get a fuller picture of the bank’s performance in these areas.
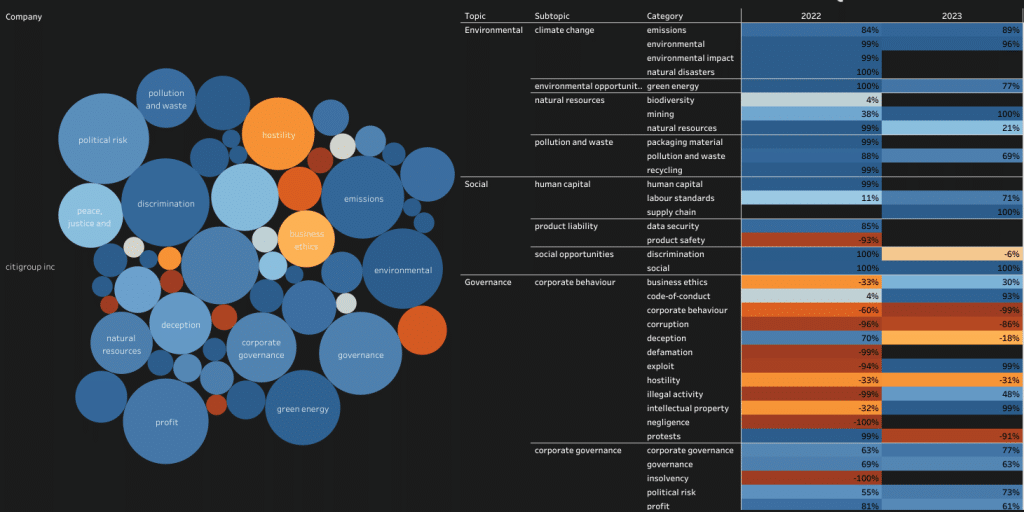
For example, while Citigroup has made impressive progress in reducing its carbon footprint and promoting diversity and inclusion, there are still areas where the bank could improve. For example, Citigroup has faced criticism for its financing of fossil fuel projects, and has been accused of failing to adequately address human rights concerns in its supply chain.
Additionally, while Citigroup has made efforts to improve its corporate governance practices in recent years, there are still concerns about the bank’s executive compensation structure and its transparency around political spending.
Investors should consider these factors and others when evaluating Citigroup’s sustainability and ethical practices, and should use multiple sources of information to get a complete picture of the bank’s performance in these areas.
Citigroup’s response to ESG rating criticisms
As with any company, Citigroup has faced criticism regarding its ESG rating, particularly with regard to its role in financing fossil fuel projects. In response, Citigroup has made a number of commitments to reduce its exposure to fossil fuels and increase its financing of renewable energy projects.
For example, Citigroup has pledged to invest $100 billion in climate solutions over the next decade, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, and sustainable transportation. The bank has also committed to reducing its exposure to coal mining and thermal coal power, and to increasing its financing of wind and solar projects.
While these commitments are certainly positive steps, some critics argue that they do not go far enough to address the urgent need to transition to a low-carbon economy. Investors should consider these criticisms and Citigroup’s response when evaluating the bank’s sustainability and ethical practices.
How investors can use ESG ratings to make informed decisions
ESG ratings can be a valuable tool for investors looking to make more informed decisions about where to put their money. However, it is important to use ESG ratings in conjunction with other sources of information, and to consider individual company performance rather than relying solely on industry averages.
Investors should also consider their own priorities and values when evaluating ESG ratings. For example, investors who prioritize environmental sustainability may place more weight on a company’s environmental score, while investors who prioritize diversity and inclusion may place more weight on its social score.
Finally, investors should be aware of the limitations of ESG ratings. While they can provide valuable information about a company’s sustainability and ethical practices, they are not a perfect measure, and there may be factors that are not captured by the rating. Investors should use ESG ratings as one tool among many when making investment decisions.
The future of ESG ratings and their role in sustainable investing
ESG ratings are likely to become an increasingly important tool for investors as the world becomes more aware of the need to prioritize sustainability and ethical practices. As more companies seek to improve their sustainability and ethical practices, ESG ratings will become an important way to evaluate their progress.
However, there are still challenges to be addressed in the ESG rating space. For example, there is currently no standardized methodology for calculating ESG ratings, which can lead to confusion and inconsistency. Additionally, there is a need for greater transparency around the data used to calculate ESG ratings, and for more rigorous evaluation of company performance.
Despite these challenges, ESG ratings are an important step forward in promoting sustainability and ethical practices among companies. As investors continue to prioritize these factors, companies will be incentivized to improve their performance in these areas, leading to a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
Conclusion
The Citigroup ESG rating is an important indicator of the bank’s sustainability and ethical practices, and provides investors with valuable information about the bank’s performance in these areas. While the rating is certainly impressive, it is important to consider Citigroup’s performance beyond the rating, and to use multiple sources of information when evaluating the bank’s sustainability and ethical practices.
As ESG ratings become an increasingly important tool for investors, it is important to use them in conjunction with other sources of information, and to consider individual company performance rather than relying solely on industry averages. With continued focus on sustainability and ethical practices, we can create a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
Access Permutable’s Granular Data for Citigroup ESG Rating
Are you an investor seeking detailed insights into Citigroup’s ESG rating and its implications for sustainability? Unlock the power of Permutable’s granular data to gain a comprehensive understanding of Citigroup’s performance in environmental, social, and governance factors.
Permutable offers in-depth analysis, utilizing cutting-edge algorithms and a vast array of data sources to provide you with accurate and actionable information. With Permutable’s data, you can assess Citigroup’s sustainability efforts beyond its ESG rating, evaluate its strengths and weaknesses, and make informed investment decisions aligned with your values and priorities.
Don’t rely solely on industry averages or surface-level information. Dive deep into Citigroup’s ESG rating with Permutable’s granular data and gain a competitive edge in the sustainable investing landscape. Get in touch to access Permutable’s granular data for Citigroup’s ESG rating as well as competitor ESG reports.
