Starbucks, the Seattle-based coffee giant, has become a household name for coffee lovers worldwide. With over 31,000 stores across the globe, Starbucks has built a brand that is synonymous with quality coffee, cozy atmosphere, and friendly customer service. But beyond its delectable brews and inviting ambiance, how does the Starbucks ESG score stack up along with the company’s ethical commitments? In this article, we delve deep into the Starbucks ESG score, exploring its commitment to environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and corporate governance.
Understanding the importance of ESG scores for businesses
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance, and it is a metric used to measure a company’s performance in these areas. ESG scores are becoming increasingly important for businesses as investors, consumers, and stakeholders are demanding more transparency and accountability. An ESG score evaluates a company based on various factors, such as its carbon footprint, social impact, diversity and inclusion, human rights, corporate governance, ethical sourcing, and supply chain management. Companies with high ESG scores are considered to be more sustainable, socially responsible, and better equipped to navigate risks and opportunities.
For Starbucks, an ESG score is critical in ensuring the company’s long-term success and relevance. Starbucks has built its brand on the pillars of quality, ethics, and sustainability, and it is expected to uphold these values in all its operations. Starbucks has set ambitious targets for reducing its carbon footprint, promoting fair trade practices, ensuring diverse and inclusive workplaces, and supporting ethical sourcing of coffee beans. By measuring its performance against ESG criteria, Starbucks can gauge its progress, identify areas of improvement, and communicate its efforts to stakeholders.
Overview of the Starbucks ESG score and ethical commitments
According to our ESG intelligence on Starbucks, the Starbucks ESG score is strongest in environmental factors (81), yet poor in social factors (30) and also governance factors (29).
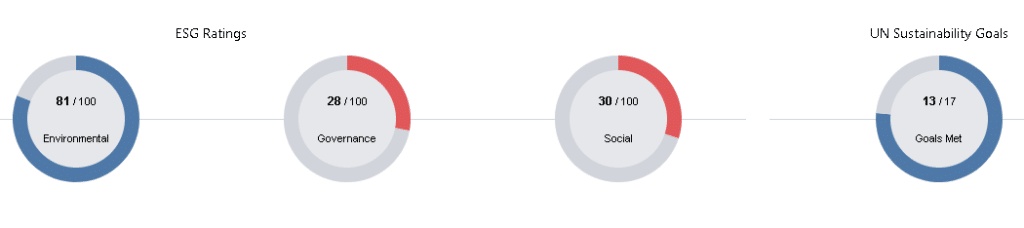
Environmental factors
Starbucks scores relatively strongly on environmental factors due to its comprehensive sustainability initiatives and commitments. The company has set ambitious goals for reducing its environmental impact, and it has made significant progress in achieving these goals.
Here are some of the reasons why Starbucks scores well on environmental factors:
-
Sustainable sourcing: Starbucks is committed to sourcing its coffee beans ethically and sustainably. The company has developed a comprehensive Coffee and Farmer Equity (C.A.F.E.) Practices program that ensures that its coffee is grown and processed in a way that is environmentally and socially responsible.
-
Waste reduction: Starbucks is working to reduce its waste footprint by using more recyclable and compostable materials. The company has also implemented a number of programs to encourage customers to reuse their cups and reduce their waste.
-
Water conservation: Starbucks is committed to conserving water in its operations. The company has implemented a number of water-saving measures, such as using high-efficiency fixtures and equipment.
-
Energy efficiency: Starbucks is working to improve the energy efficiency of its stores. The company has implemented a number of energy-saving measures, such as using LED lighting and energy-efficient appliances.
-
Climate change: Starbucks is committed to addressing climate change. The company has set a goal of becoming resource positive, which means storing more carbon than it emits, water positive, and reducing waste sent to landfills by 50% by 2030.
Despite its strong environmental performance, there is still room for improvement for Starbucks. Some areas where the company could improve include:
-
Reducing its reliance on single-use cups: Starbucks still uses a large number of single-use cups, which contribute to waste and pollution. The company could encourage customers to bring their own reusable cups or offer more incentives for using reusable cups.
-
Reducing its carbon footprint: Starbucks could further reduce its carbon footprint by investing in renewable energy and electrifying its fleet of vehicles.
Social factors
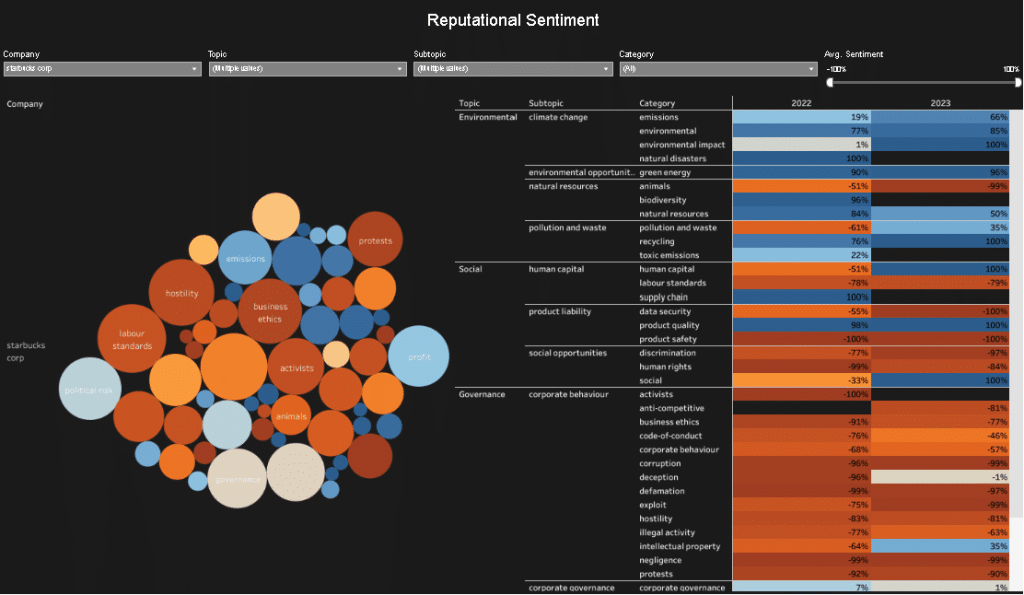
Starbucks has faced criticism for its social practices, particularly in the areas of labour relations and community engagement. While the company has made some efforts to address these concerns, there is still room for improvement.
Labour Relations:
-
Unionization Efforts: Starbucks has been criticized for its efforts to discourage unionization among its employees. The company has been accused of using anti-union tactics, such as holding captive audience meetings and firing union organizers.
-
Wages and Benefits: Starbucks has also been criticized for its relatively low wages and benefits, particularly for its baristas. While the company has raised wages in recent years, some argue that it still does not pay its employees a living wage.
Community Engagement:
-
Gentrification: Starbucks has been accused of contributing to gentrification in some neighbourhoods. The company’s presence can drive up property values and rents, making it harder for low-income residents to afford to live in those areas.
-
Corporate Social Responsibility: While Starbucks has a corporate social responsibility program, some critics argue that it does not do enough to address social issues in the communities where it operates.
Starbucks’ Efforts to Improve:
-
Unionization: Starbucks has recently pledged to take a more neutral stance on unionization and to respect the right of its employees to organize.
-
Wages and Benefits: Starbucks has raised wages in recent years and has also expanded its benefits package to include things like paid parental leave and tuition reimbursement.
-
Community Engagement: Starbucks has launched a number of initiatives to support local communities, such as its Neighborhood Grants program and its Community Store program.
Overall, Starbucks has made some progress in addressing its social shortcomings, but there is still room for improvement. The company should continue to work to improve its labour relations and community engagement efforts to improve its social score.
Governance factors
Starbucks scores relatively low on governance factors due to concerns about its board diversity, executive compensation, and shareholder rights.
-
Board Diversity: Starbucks’ board of directors lacks diversity in terms of gender, race, and ethnicity. While the company has made some progress in recent years, its board is still not as diverse as it could be.
-
Executive Compensation: Starbucks’ executive compensation has been criticized for being excessive. The company’s CEO, Howard Schultz, is one of the highest-paid CEOs in the world.
-
Shareholder Rights: Starbucks has been criticized for its lack of shareholder rights. The company’s dual-class share structure gives its founders and insiders more voting power than other shareholders.
Examples of specific criticisms of Starbucks’ governance practices:
-
In 2022, Starbucks faced criticism for its decision to award CEO Kevin Johnson a $60 million pay package, despite the company’s relatively poor financial performance during his tenure.
-
In 2023, Starbucks was sued by a group of shareholders who alleged that the company’s dual-class share structure disenfranchises minority shareholders.
Starbucks has taken some steps to address these concerns, such as increasing the number of women and minorities on its board of directors. However, the company still has more work to do to improve its governance practices.
Here are some specific recommendations for how Starbucks could improve its governance practices:
-
Further diversify its board of directors to include more women, minorities, and independent directors.
-
Tie executive compensation more closely to company performance.
-
Give all shareholders equal voting rights.
By taking these steps, Starbucks could improve its corporate governance and better align its practices with the interests of all of its stakeholders.
Comparison of Starbucks’ ESG score with competitors in the coffee industry
When comparing the Starbucks ESG score to that of its competitors in the coffee industry, a clear trend emerges: Starbucks typically maintains a higher ESG score. This score is a reflection of their exposure to ESG risks and opportunities, as well as their management of ESG issues. However, there are exceptions to this pattern, as illustrated by the Costa Group’s ESG score, which surpasses Starbucks in certain aspects.
Starbucks’ Strong ESG Score: Starbucks has been a frontrunner in integrating ESG considerations into its business operations. It demonstrates a robust commitment to environmental sustainability, ethical sourcing, and responsible business practices. Its ESG score often reflects these efforts, making it a benchmark for corporate responsibility within the coffee industry.
The Costa Group’s Exceptional Performance: The Costa Group, which boasts a strong ESG score, stands as an exception to Starbucks’ usual dominance. This company, known for its ethical sourcing and sustainable practices, has achieved notable success in certain areas that contribute to its higher ESG rating particularly in environmental and governance factors, though Costa’s social score is comparable. Take a look at Costa’s ESG score.
McDonald’s Comparable ESG Score: McDonald’s, although primarily a fast-food giant, operates within the same competitive landscape as Starbucks and has a comparable ESG score. This score reflects McDonald’s ongoing efforts to improve its ESG performance, particularly concerning its environmental impact and supply chain management. Take a look at McDonald’s ESG score.
Specialty Coffee Companies: Smaller, specialty coffee companies sometimes outshine Starbucks in particular aspects of their ESG performance. For instance, these companies may excel in their commitment to sourcing coffee beans from small-scale farmers, promoting organic and shade-grown coffee, or championing sustainable farming practices. While they may not have the same global reach as Starbucks, their focused approach to specific ESG criteria allows them to achieve higher scores in these areas.
Criticisms and controversies surrounding Starbucks’ ethical commitments
Despite its efforts to be a socially responsible company, Starbucks has faced criticisms and controversies over the years. In 2018, Starbucks faced backlash after two black men were arrested at a Philadelphia store for sitting without ordering anything. The incident sparked nationwide protests and forced Starbucks to close its stores for a day to conduct racial bias training for its employees. Starbucks has since implemented several measures to address racial bias and promote diversity and inclusion, such as anti-bias training, diversity hiring, and community outreach programs.
In addition, Starbucks has faced criticism over its sourcing practices, particularly in relation to fair trade and labour rights. Some activists argue that Starbucks should pay higher prices to coffee farmers and improve working conditions in its supply chain. Starbucks has responded by increasing its investment in farmer support centers, promoting sustainable farming practices, and sourcing from certified farms.
The impact of Starbucks’ ESG score on consumer perception and loyalty
Starbucks’ commitment to sustainability and social responsibility has a significant impact on its brand image and customer loyalty. Many consumers today are willing to pay a premium for products that are environmentally friendly, socially responsible, and ethically sourced. By scoring high on ESG metrics, Starbucks can attract and retain customers who value these attributes.
In addition, Starbucks’ ESG performance can also influence investor decisions. Many investors today are looking for companies that are well-positioned to navigate ESG risks and opportunities. By demonstrating its commitment to ESG criteria, Starbucks can attract socially responsible investors who are interested in generating both financial returns and positive social and environmental impacts.
Conclusion: Evaluating Starbucks’ overall commitment to sustainability and social responsibility
In conclusion, while Starbucks has made significant progress in improving its ESG performance and ethical commitments setting ambitious targets for reducing its environmental footprint, promoting social inclusion, and ensuring ethical sourcing of coffee beans there is still plenty of work to be done particularly in areas such as fair trade practices and labour rights. Starbucks must continue to monitor its ESG performance, identify areas of improvement, and communicate its efforts to stakeholders. By doing so, Starbucks can build a stronger brand, attract and retain customers, and contribute to a more sustainable and socially responsible future.
Ready to dive deeper into the data behind Starbucks’ ESG performance? Unlock the potential for more granular insights on Starbucks by reaching out to Permutable AI. Contact us at enquiries@permutable.ai or simply complete the form below.