In the fast-paced world of business, the supply chain serves as the silent conductor orchestrating the symphony of procurement, production, distribution, and delivery. Yet, with the growing spotlight on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues, the words supply chain transparency and traceability have become the guiding stars for companies navigating the expectations of consumers, investors, regulators, and stakeholders. In this article we will explore the evolution of supply chain transparency, delve into the challenges faced, and understand the benefits of embracing this transformative commitment.
Introduction to Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Supply chain transparency is the lifeline that breathes accountability into a company’s supply chain activities. It’s about making these activities visible, accountable, and communicated to stakeholders, from identifying risks to disclosing performance metrics related to ESG issues. However, it’s not just about paperwork – it’s a dance of engagement with suppliers, customers, investors, and other stakeholders, fostering trust, collaboration, and continuous improvement. In an era where consumers demand transparency and traceability, it has become a competitive advantage and a crucial element for enhancing reputation and creating value.
The Importance of Supply Chain Due Diligence
Supply chain due diligence is the key to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks related to ESG issues. It involves mapping the supply chain, screening suppliers, auditing their performance, and monitoring compliance with standards and regulations. Compliance with acts such as the California Transparency in Supply Chains Act, the UK Modern Slavery Act, and the EU Conflict Minerals Regulation is not only a legal requirement but a moral obligation to ensure products are ethically produced.
The Evolution of Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
The journey of supply chain transparency began in the early 2000s, with pioneering companies disclosing information about their supply chain practices. However, it wasn’t until the mid-2010s, sparked by incidents like the Rana Plaza factory collapse in 2013, that transparency transformed from a compliance issue into a strategic imperative. Investors now weave supply chain transparency into the fabric of ESG investing, calling for increased disclosure and accountability.
Current Challenges in Achieving Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Achieving supply chain transparency and traceability is a commendable goal, yet companies encounter significant challenges in navigating this complex terrain. These challenges pose hurdles that, if not addressed effectively, can impede the seamless integration of transparent practices into the supply chain.
Lack of Visibility Beyond the First Tier of Suppliers
One of the primary challenges is the lack of visibility beyond the first tier of suppliers. Supply chains are often intricate webs involving multiple layers of suppliers, subcontractors, and manufacturers. Obtaining comprehensive visibility into these extended tiers can be daunting. Limited transparency beyond the initial tier may result in a partial understanding of potential risks and environmental impacts further down the supply chain. Addressing this challenge requires collaborative efforts, as companies must encourage suppliers to disclose information not only about their direct suppliers but also the subsequent tiers, fostering a culture of transparency throughout the entire network.
The Complexity of Mapping and Monitoring Intricate Supply Chains
The sheer complexity of mapping and monitoring intricate supply chains adds another layer of difficulty. Modern supply chains are global, interconnected, and multifaceted, involving a multitude of processes, geographical locations, and stakeholders. Mapping these complexities in real-time requires advanced technologies, data analytics, and a collaborative approach with suppliers. It demands an investment in digital tools and platforms that can provide a comprehensive overview of the entire supply chain, enabling efficient monitoring and risk assessment.
Supplier Resistance to Disclosing Information or Improving Sustainability Practices
Resistance from suppliers to disclose information or improve sustainability practices represents a significant roadblock. Some suppliers may be hesitant to share data due to concerns about revealing proprietary information, while others may lack the resources or capabilities to meet transparency standards. Overcoming this challenge necessitates clear communication, education, and incentives for suppliers. Companies can foster a cooperative environment by emphasising the mutual benefits of transparency, such as improved efficiency, reduced risks, and long-term collaboration. Implementing supplier engagement programs and providing support for sustainability improvements can help overcome resistance.
The Financial Burden of Implementing Transparency and Traceability, Particularly for SMEs
Implementing transparency and traceability measures incurs a financial burden, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). SMEs may lack the resources, both financial and technological, required to invest in advanced traceability systems. The cost of implementing these technologies, conducting audits, and ensuring compliance with transparency standards can be a barrier. To address this, larger companies can support their SME suppliers by providing resources, offering training, and establishing cooperative initiatives. Collaborative industry efforts and government support can also play a role in easing the financial strain on smaller enterprises.
Addressing Ethical Concerns in Supply Chains
One of the most pressing issues in supply chain transparency is the detection and elimination of forced labour. Companies are increasingly implementing robust management systems to monitor their entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. These systems are designed to identify potential human rights violations and ensure ethical practices throughout the supply chain. When issues are detected, companies must take swift corrective action, which may include terminating relationships with suppliers found to be using forced labour, implementing stricter monitoring protocols, or providing training and support to improve working conditions. By focusing on ethical sourcing and maintaining vigilant oversight, businesses can work towards eradicating forced labour from their supply chains, thereby enhancing their reputation and meeting the growing demand for ethically produced goods.
The Benefits of Embracing Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Embracing supply chain transparency and traceability yields a diverse range of benefits that extend beyond mere compliance. Companies that actively integrate these principles into their operations stand to gain significantly in terms of reputation, risk management, innovation, collaboration, and cost efficiency.
Enhanced Reputation through Transparent Practices
Demonstrating a commitment to transparency in the supply chain enhances a company’s reputation. In an era where consumers are increasingly conscious of the origins and ethical aspects of products, transparent practices create trust. When stakeholders, including customers and investors, can trace the journey of a product and verify its ethical and sustainable attributes, it fosters a positive perception of the company. This enhanced reputation can contribute to brand loyalty and attract consumers who prioritise ethical and sustainable choices.
Efficient Risk Management by Identifying and Mitigating Potential Issues
Supply chain transparency serves as a proactive risk management tool. By identifying and understanding every step in the supply chain, companies can pinpoint potential vulnerabilities and risks. Whether these risks involve compliance issues, environmental concerns, or geopolitical factors, early detection allows for strategic mitigation. This proactive approach not only safeguards the company against potential disruptions but also demonstrates a commitment to responsible business practices, further reinforcing trust among stakeholders.
Driving Innovation and Collaboration among Suppliers for Sustainable Products
Transparency encourages innovation within the supply chain. When companies share information about their sustainability goals and initiatives, it sets the stage for collaborative efforts with suppliers. This collaboration can lead to the development of sustainable products, processes, and materials. Suppliers, motivated by the demand for transparency, are incentivised to adopt more sustainable practices, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. The drive for innovation within the supply chain contributes not only to the company’s environmental footprint but also to its competitiveness in a market increasingly valuing sustainability.
Identifying Cost-Saving Opportunities through Supply Chain Optimization
Transparent supply chains enable companies to optimise their operations and identify cost-saving opportunities. By having a comprehensive view of the entire supply chain, companies can streamline processes, reduce waste, and identify areas for efficiency improvements. This optimisation not only results in direct cost savings but also contributes to a more sustainable and resource-efficient supply chain. Companies that leverage transparency for supply chain optimisation can achieve a balance between economic efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Key Trends and Technologies in Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Several trends and technologies are steering the evolution of supply chain transparency:
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain has emerged as a game-changer for secure and transparent product tracking in the supply chain. Its decentralized and tamper-resistant nature ensures that once information is recorded, it cannot be altered. This makes it ideal for creating an immutable record of every transaction and movement within the supply chain, offering stakeholders unparalleled visibility and trust in the data.
Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
The Internet of Things has brought about a revolution in supply chain management by providing real-time data on product conditions. IoT devices, such as sensors and trackers, can be embedded in products or packaging, enabling companies to monitor variables like temperature, humidity, and location throughout the entire journey of goods. This real-time data is invaluable for ensuring product quality, identifying potential issues, and maintaining optimal conditions.
Artificial Intelligence
AI is playing a pivotal role in analysing vast amounts of data to facilitate informed decision-making in the supply chain. Machine learning algorithms like those at the heart of Permutable AI’s real-time supply chain monitoring can sift through complex datasets to identify patterns, trends, and potential risks. In the context of transparency, AI can help in assessing supplier performance, predicting supply chain disruptions, and even identifying areas for improvement in sustainability practices.
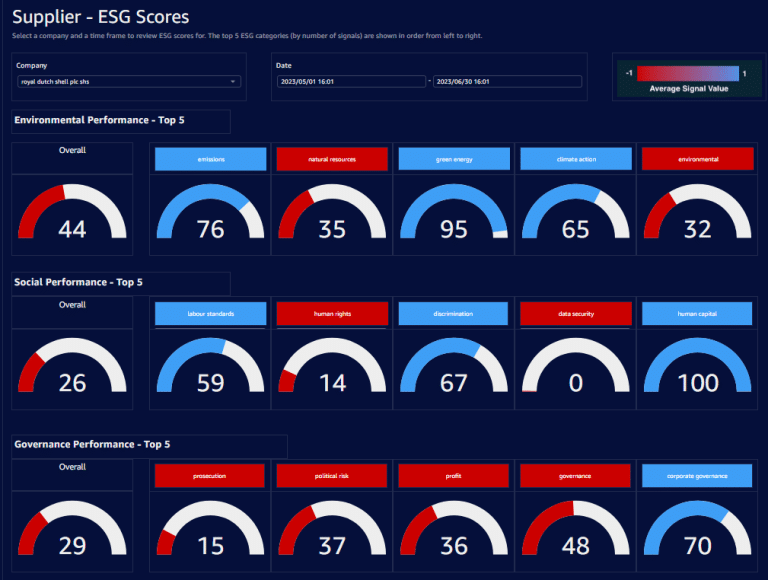
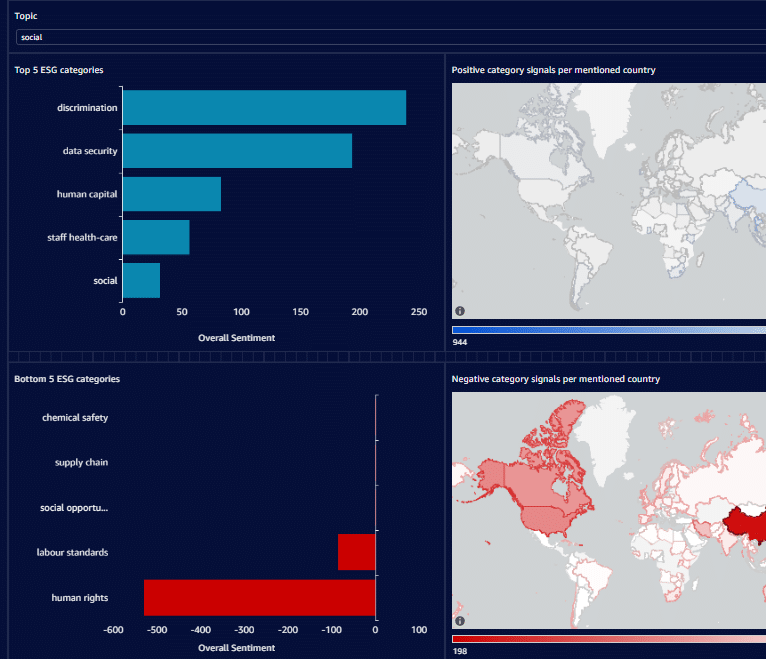
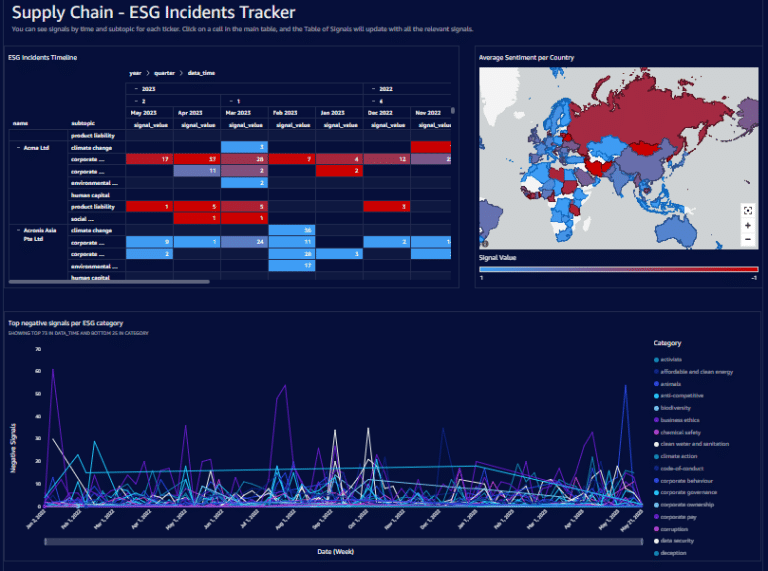
Collaborative Platforms
Collaborative platforms dedicated to sustainability and ethical practices, such as EcoVadis and Sedex, are fostering transparency and trust in supply chains. These platforms act as intermediaries, allowing companies to share and access information about suppliers’ social, environmental, and ethical performance. By bringing together diverse stakeholders, these platforms encourage a collaborative approach to transparency, helping companies make informed decisions about their supply chain partners.
Embracing these trends and technologies is not just about staying current; it’s a strategic move to enhance supply chain visibility, build trust, and meet the growing expectations of consumers and stakeholders. As companies navigate the complexities of the modern supply chain, leveraging these innovations becomes crucial for staying ahead in an era where transparency is synonymous with responsible business practices.
Steps to Transition from Compliance to Commitment
Successfully transitioning from mere compliance to a genuine commitment to supply chain transparency is a multifaceted journey that requires strategic planning, collaboration, and a cultural shift within an organisation. Here are the key steps for companies aiming to make this transition:
Set Ambitious Goals for Transparency and Traceability
The foundation of a commitment to supply chain transparency lies in setting ambitious and clear goals. These goals should encompass not only compliance with existing regulations but also surpass them to meet higher standards. Companies should define specific targets related to visibility, sustainability, and traceability throughout their supply chain. These goals become the guiding principles for the entire transparency initiative.
Engage with Suppliers to Understand and Improve Sustainability Practices
Collaboration with suppliers is pivotal in the journey towards commitment. Companies need to actively engage with their suppliers to gain a comprehensive understanding of their sustainability practices. This involves open communication, sharing expectations, and fostering a collaborative approach to improve sustainable practices collectively. Establishing a two-way dialogue helps build trust, encourages suppliers to embrace transparency, and creates a shared commitment to ethical and sustainable supply chain practices.
Leverage Technology Such as Blockchain, IoT, and AI
Embracing cutting-edge technologies is essential for achieving advanced levels of transparency and traceability. Companies should invest in technologies like blockchain for secure and transparent product tracking, Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time data on product conditions, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) for analysing data to make informed decisions. These technologies not only enhance visibility but also contribute to more sustainable and efficient supply chain management.
Foster a Culture of Transparency Across the Organization
Transitioning to a commitment to transparency requires a cultural shift within the organisation. This involves instilling transparency as a core value and integrating it into the organisational culture. Leadership plays a crucial role in fostering this culture by setting an example, communicating the importance of transparency, and integrating it into performance metrics. Training programs and internal communication initiatives can help employees understand their role in the commitment to supply chain transparency.
Communicate Transparently with Stakeholders About Supply Chain Practices
Transparent communication is vital for building trust among stakeholders, including customers, investors, and the broader community. Companies should develop clear and accessible communication channels to share information about their supply chain practices. This involves creating sustainability reports, sharing progress towards goals, and addressing challenges openly. Transparent communication not only demonstrates a commitment to accountability but also allows stakeholders to make informed decisions and hold the company accountable for its sustainability commitments.
Case Studies
Examples of successful implementation of supply chain transparency and traceability include:
Nestle’s Blockchain for Traceability and Responsible Sourcing:
Nestle has emerged as a leader in leveraging blockchain technology to enhance traceability and promote responsible sourcing in its supply chain. By implementing blockchain, Nestle ensures a secure and transparent system for tracking its products from source to shelf. This technology allows the company to trace the journey of raw materials, such as coffee or cocoa, through every stage of the supply chain. Nestle’s commitment to responsible sourcing is further exemplified by its adoption of a Responsible Sourcing Standard, setting clear guidelines and expectations for suppliers to adhere to ethical and sustainable practices. This comprehensive approach not only strengthens Nestle’s supply chain transparency but also demonstrates a commitment to ethical sourcing practices.
Patagonia’s Supply Chain Mapping and Supplier Engagement:
Patagonia, the renowned outdoor apparel company, has undertaken a commendable initiative by mapping its entire supply chain and actively engaging with suppliers to improve sustainability. By meticulously mapping each stage of its supply chain, Patagonia gains a comprehensive understanding of the environmental and social impacts associated with its products. This detailed mapping enables the company to identify areas for improvement and implement sustainable practices. Furthermore, Patagonia goes beyond mere compliance by engaging directly with its suppliers, fostering collaboration, and providing support to enhance sustainability measures. This hands-on approach not only ensures transparency but also contributes to a culture of continuous improvement and responsible sourcing within the company’s supply chain.
Unilever’s Ambitious Goals for Traceability and Enhanced Transparency:
Unilever, the global consumer goods giant, has set ambitious goals for traceability and embraced technology to achieve enhanced transparency in its supply chain. Unilever’s commitment to traceability involves the use of advanced technologies such as blockchain and satellite monitoring to track the origin and journey of key ingredients. By leveraging these technologies, Unilever can verify the sustainability claims associated with its products and provide consumers with clear information about the sourcing of raw materials. Additionally, Unilever’s use of technology goes hand in hand with the company’s broader goals for enhancing transparency across its supply chain. The combination of setting ambitious traceability targets and adopting advanced technologies showcases Unilever’s dedication to leading the way in responsible and transparent supply chain practices.
These examples highlight how companies like Nestle, Patagonia, and Unilever are not only adopting advanced technologies for traceability but also integrating responsible sourcing standards, supply chain mapping, and direct supplier engagement into their strategies. By doing so, these companies are not just meeting compliance requirements but are proactively shaping the industry towards ethical and sustainable supply chain practices.
The Future of Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability in 2024
Looking ahead to 2024, we anticipate:
Increased Regulations Requiring More Disclosure
As we approach 2024, a notable trend in the future of supply chain transparency is the anticipation of increased regulations demanding higher levels of disclosure. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are recognising the significance of transparent and ethical supply chains. This recognition is likely to translate into the formulation and enforcement of more stringent regulations. Companies operating in diverse industries will face a growing legal mandate to disclose detailed information about their supply chain practices, sustainability efforts, and adherence to ethical standards. This shift reflects a global commitment to holding businesses accountable for their social and environmental impact, encouraging a more responsible approach to supply chain management.
Greater Use of Technology to Enhance Transparency
The future of supply chain transparency is intrinsically linked to technological advancements. In 2024, we anticipate a surge in the adoption and integration of cutting-edge technologies to enhance transparency throughout the supply chain. Blockchain technology, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) will play pivotal roles in providing real-time, secure, and data-driven insights into supply chain activities. Blockchain’s ability to create an immutable and transparent ledger will be harnessed for secure product tracking, while IoT devices will contribute by offering real-time data on product conditions. AI, with its data analysis capabilities, will be employed for informed decision-making, further enriching the transparency landscape and ensuring a more comprehensive understanding of supply chain dynamics.
More Collaboration Among Companies, Suppliers, and Civil Society
Collaboration is set to be a cornerstone of the future supply chain landscape in 2024. Companies, suppliers, and civil society are expected to engage in deeper collaborative efforts to foster transparency and ethical practices. Industry leaders will recognise the interconnectedness of supply chains and the shared responsibility for sustainable and ethical sourcing. Collaborative platforms, industry consortia, and partnerships will emerge as mechanisms for sharing best practices, conducting joint audits, and collectively addressing challenges. This collaborative approach is essential not only for addressing complex supply chain issues but also for creating a collective impact that goes beyond individual corporate boundaries.
Heightened Stakeholder Expectations for Transparency and Accountability
The expectations of stakeholders, including consumers, investors, and advocacy groups, are anticipated to reach new heights in terms of transparency and accountability. As awareness around environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues continues to grow, stakeholders will demand more comprehensive disclosures and measurable actions from businesses. Companies will face increasing pressure to not only meet regulatory requirements but to exceed them and proactively address concerns related to sustainability, human rights, and ethical business practices. This heightened scrutiny will prompt businesses to embrace transparency not merely as a compliance measure but as a fundamental aspect of their commitment to responsible and sustainable operations.
Final Thoughts
Supply chain transparency and traceability are not merely buzzwords but essential components of a company’s strategic framework. Embracing these concepts can elevate reputation, manage risks, foster innovation, and create lasting value. Despite challenges, transitioning from compliance to commitment involves setting goals, engaging with suppliers, leveraging technology, nurturing a transparent culture, and communicating openly with stakeholders. By adopting best practices and learning from case studies, companies can navigate the ever-evolving landscape of supply chain transparency and prepare for a future where commitment, not just compliance, is the key to success.
Find Out More
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, where supply chains weave intricate patterns in the global marketplace, ensuring transparency and traceability is not just a necessity but a strategic imperative. At Permutable AI, we understand the evolving challenges and opportunities in supply chain management, and our AI-powered solutions are designed to empower your business with real-time monitoring and actionable insights.
If you’re ready to embrace a future where your supply chain is not just compliant but a beacon of commitment to transparency, we invite you to take the next step. Reach out to us at enquiries@permutable.ai or fill out the form to discover how our cutting-edge AI technologies can revolutionise your supply chain. Let’s shape a future where transparency is not just a buzzword, but a driving force behind your company’s success. Contact us today to embark on a transformative journey towards a more sustainable, responsible, and transparent supply chain.