Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) scores have gained significant attention in recent years as investors, businesses, and consumers focus on sustainable practices and responsible corporate behaviour. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the importance of ESG scores, their components, and how they can affect a company’s reputation and financial performance.
Table of Contents
ToggleTable of Contents
What are ESG Scores?
The Three Pillars of ESG: Environmental, Social, and Governance
Why ESG Scores Matter
ESG Rating Agencies and Methodologies
Improving ESG Scores: Strategies for Companies
ESG Scores and Investment Decisions
The Future of ESG Investing
What are ESG Scores?
ESG scores are a measure of a company’s performance in three key areas: environmental, social, and governance. They provide a comprehensive assessment of a company’s sustainability and ethical practices, helping investors and other stakeholders make informed decisions about the businesses they engage with.
These scores are generated by ESG rating agencies using standardised methodologies, which consider a wide range of factors such as carbon emissions, labor practices, and board diversity. By comparing ESG scores, investors can gauge a company’s commitment to responsible practices and long-term value creation.
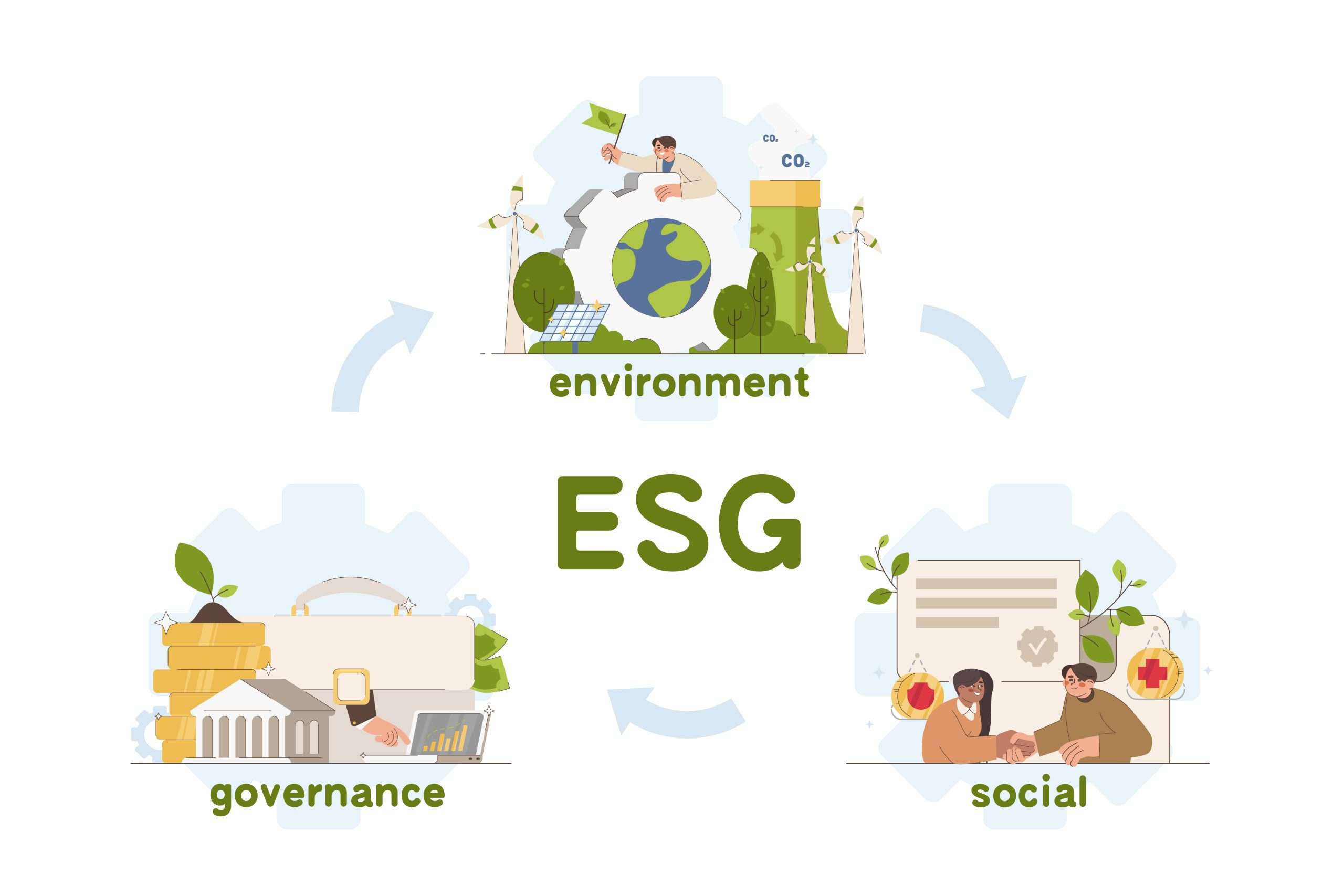
The Three Pillars of ESG: Environmental, Social, and Governance
ESG scores are based on three main pillars: environmental, social, and governance. Each pillar encompasses specific criteria used to evaluate a company’s performance.
Environmental
The environmental pillar focuses on a company’s impact on the environment, including:
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Waste management
- Energy efficiency
- Natural resource conservation
- Climate change risks and opportunities
Social
The social pillar considers a company’s relationships with employees, customers, and communities, including:
- Labor practices and human rights
- Health and safety
- Diversity and inclusion
- Customer satisfaction and privacy
- Community engagement and development
Governance
The governance pillar examines a company’s management structure and decision-making processes, including:
- Board composition and independence
- Executive compensation
- Shareholder rights
- Business ethics and transparency
- Risk management
Why ESG Scores Matter
ESG scores matter for several reasons:
Risk management: Companies with strong ESG performance are better equipped to manage environmental, social, and governance risks, reducing the likelihood of financial losses or reputational damage.
Long-term value creation: Companies that prioritise ESG factors tend to focus on long-term growth and sustainability, making them more attractive to investors.
Regulatory compliance: As regulations around sustainability and corporate responsibility evolve, companies with high ESG scores are better positioned to meet these requirements.
Consumer preferences: Consumers increasingly prefer companies that demonstrate a commitment to responsible practices, which can lead to higher brand loyalty and market share.
Talent attraction and retention: Companies with strong ESG performance are more likely to attract and retain top talent, resulting in a more productive and innovative workforce.
ESG Rating Agencies and Methodologies
Improving ESG Scores: Strategies for Companies
Environmental
- Set and track sustainability goals, such as reducing emissions, waste, or water consumption.
- Implement energy efficiency measures and invest in renewable energy sources.
- Adopt green supply chain practices and engage with suppliers on sustainability.
- Develop products and services that promote environmental stewardship.
Social
- Create a diverse and inclusive workplace culture, providing equal opportunities for all employees.
- Implement strong labor practices and ensure compliance with human rights standards.
- Establish health and safety policies and procedures, prioritising employee well-being.
- Engage with local communities and support community development initiatives.
Governance
- Ensure board composition includes diverse perspectives and independent oversight.
- Establish transparent executive compensation policies tied to performance and ESG metrics.
- Strengthen shareholder rights and promote effective communication with investors.
- Implement robust risk management processes, focusing on ESG-related risks.