It goes without saying that in today’s complex business environment, ensuring ethical and sustainable supply chains is a non-negotiable for maintaining corporate responsibility and customer trust. With that said, in this case study, we will explore the use case of AI for supply chain due diligence using Permutable AI’s proprietary technology and our Tesco dataset as an example. Not interested in Tesco? Not to worry. Our innovative technologies and data intelligence can be used to replicate this for any other company to monitor and improve its supply chain performance across various environmental, social, and governance -or ESG metrics.
Table of Contents
ToggleComprehensive data integration
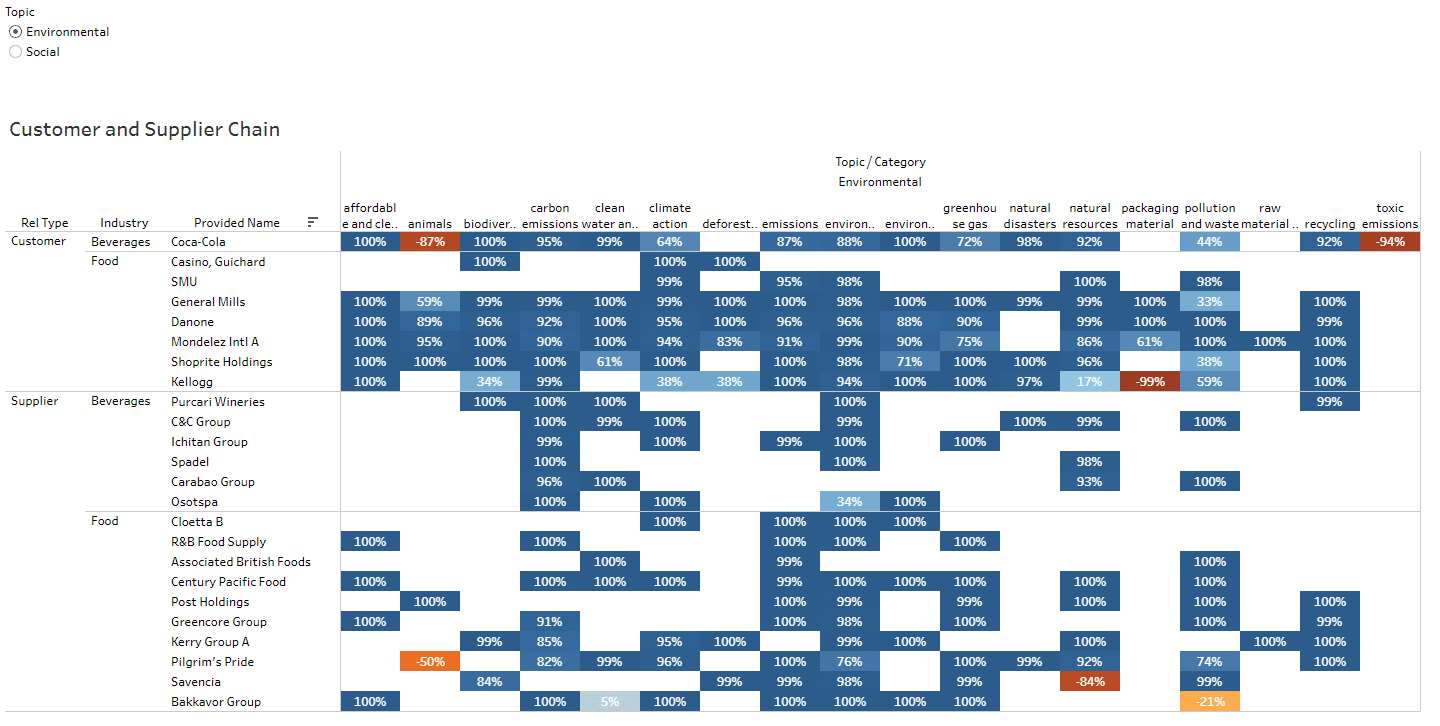
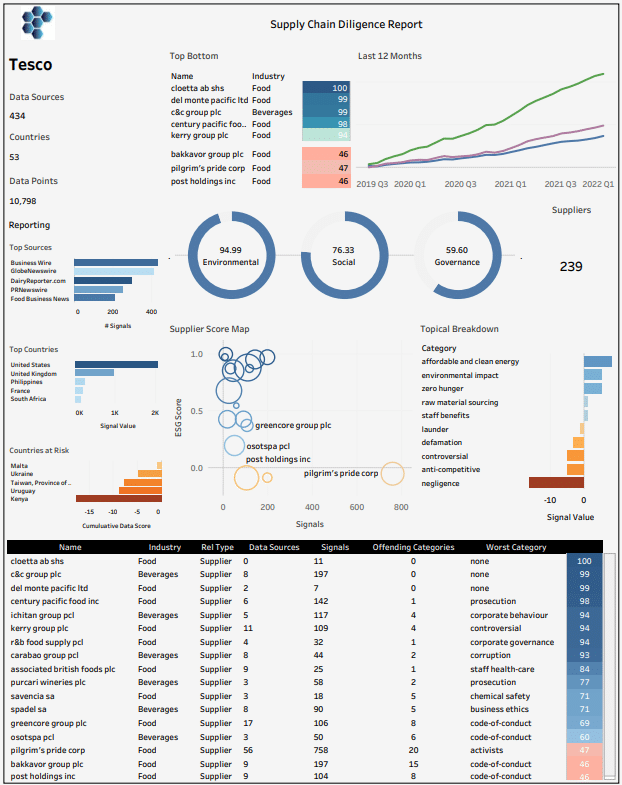
Let’s start at the beginning. At the heart of this Tesco supply chain due diligence example is the integration of diverse data sources. Using AI for supply chain due diligence, we collected data from 434 sources across 53 countries, encompassing over 10,798 data points for this study. This comprehensive data integration includes environmental reports, regulatory filings, and real-time monitoring systems, ensuring no critical data points are overlooked. The system also leverages natural language processing (NLP) to analyze unstructured data from news articles, providing a holistic view of each supplier’s performance.
Key performance metrics
This example supply chain due diligence report evaluates Tesco’s suppliers based on environmental, social, and governance criteria. The top performers include Cloetta (food industry, score: 100) and Del Monte (food industry, score: 99), demonstrating robust sustainability and ethical practices. These companies not only adhere to regulatory standards but also set higher benchmarks for environmental and social governance. In this case, using AI for supply chain due diligence would allow for these top performers to serve as benchmarks, helping to elevate overall performance by sharing best practices with other suppliers.
Conversely, Pilgrim’s Pride (food industry, score: 46) and Post Holdings Inc (food industry, score: 47) are identified as areas of concern, particularly in governance and code-of-conduct issues. Using AI for supply chain due diligence provides an avenue to detect suppliers falling short on ESG standards enabling direct engagement to address deficiencies, setting clear improvement targets and conducting regular audits. This proactive approach ensures suppliers across a supply chain such as Tesco’s meet the high standards expected, reducing risks to supply chain integrity and brand reputation. Again, this can be replicated for any company and its supply chain.
Environmental Performance
So where do things stand environmentally speaking? The report reveals an impressive environmental score of 94.99 for Tesco’s supply chain according to our analysis, indicating strong compliance with environmental standards. Suppliers are engaging in practices that reduce carbon footprints, manage waste efficiently, and use renewable resources. This is good news. Using AI for supply chain due diligence enables the tracking, maintenance of this score, by encouraging innovation in green technologies and providing incentives for significant environmental milestones.
Social and governance scores
Next, social and governance. While the environmental score is high, there is room for improvement in social (76.33) and governance (59.60) metrics. These scores suggest areas where Tesco’s supply chain can improve labour practices, diversity and inclusion, and corporate ethics. Using AI for supply chain due diligence, shines a lights on where stricter standards should be put in place for suppliers in this use case and where transparency initiatives, such as public reporting of social and governance metrics, could be used to build trust and drive improvements to ensures suppliers meet high social and governance standards.
Supplier analysis and intervention
So then, the Supplier Score Map highlights varying levels of performance among suppliers. Companies like Greencore Group show high ESG scores, while others like Pilgrim’s Pride lag behind. In this case, using AI for supply chain due diligence would facilitate the development of a tiered support system, offering intensive support to lower-performing suppliers and recognizing high performers. Regular reviews and performance assessments could be put in place to ensure continuous improvement and compliance, leveraging high-performing suppliers to mentor and share best practices.
Addressing key issues by category
The report categorizes key issues such as affordable and clean energy, environmental impact, and raw material sourcing, highlighting where Tesco and its suppliers focus their sustainability efforts. From our analysis in this example, it’s clear to see that Tesco prioritizes these areas, investing in technologies and practices that support clean energy use, sustainable sourcing, and overall environmental impact reduction. Collaborative projects with suppliers drive industry-wide improvements, ensuring Tesco remains a leader in sustainability – a smart move by the industry leader by all accounts.
Geographical insights and risk management
The example report identifies top countries providing data signals, including the United States, United Kingdom, Philippines, and South Africa, and highlights countries at risk such as Malta, Bulgaria, and Kenya. Using AI for supply chain due diligence reveals geographical areas of weakness in real time, signalling where engaging with suppliers in high-risk countries to address and mitigate specific issues is absolutely crucial to ensure compliance, thereby improving supply chain resilience. Ultimately, this knowledge will facilitate geographic-specific strategies and tailored interventions to the unique challenges and regulatory environments of each region, enhancing overall performance.
In this scenario, this example report shows how companies can leverage our insights and how by using AI for supply chain due diligence they are better positioned to make informed decisions that enhance supply chain operations, ensure ethical practices, and maintain high standards of corporate responsibility. Using Tesco here as example, it is clear that a continued focus on tracking environmental performance, improving social and governance metrics, and addressing regional risks strengthens across the supermarket giant’s sustainability initiatives would improve overall supply chain and business resilience.
This case study give a sense of the transformative power of AI in creating a more transparent, accountable, and sustainable supply chain. If you are curious to find out more and would like to see how this can be applied to your company, customers and suppliers across your supply chain then we will be happy to help. Get in touch below to discover how our technology, data intelligence and insights can assist you.