In an increasingly interconnected global economy, supply chains have become more complex, spanning multiple countries and involving numerous suppliers. With this complexity and increasing regulation comes the responsibility to ensure that human rights are respected throughout the supply chain. Identifying human rights risks is a crucial step in creating an ethical and sustainable supply chain. This article aims to provide insights into effective approaches and practical strategies for identifying human rights risks in your supply chain.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstand the Scope of Human Rights Risks
To effectively identify human rights risks, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the range of human rights issues that can arise in a supply chain. These can include forced labour, child labour, unsafe working conditions, discrimination, and environmental degradation. Familiarize yourself with international human rights standards and conventions to develop a robust framework for assessing risks.
Map Your Supply Chain
Mapping your supply chain is an important starting point for identifying potential human rights risks. Gain visibility into your suppliers, sub-contractors, and other stakeholders involved in the supply chain. Assess their geographical locations, labour practices, and potential exposure to high-risk areas or industries. This mapping exercise helps identify vulnerable points and enables targeted risk assessments.
Conduct Risk Assessments To Identify Human Rights Risks in Your Supply Chain
Implement a systematic and ongoing process of risk assessments to identify potential human rights risks. This involves analyzing available data, engaging with suppliers and workers, and utilizing external resources such as audits and certifications. Evaluate each supplier’s policies, practices, and performance against human rights criteria. Prioritize high-risk areas and suppliers for more in-depth assessments.
Engage with Suppliers and Stakeholders
Meaningful engagement with suppliers and stakeholders is vital in identifying human rights risks. Foster open communication channels to encourage dialogue and gain insights into their practices and challenges. Conduct regular site visits and worker interviews to gather first-hand information. Collaborate with industry associations, civil society organizations, and human rights experts to leverage their expertise and perspectives.
Leverage Technology and Data Analytics
Harness the power of technology and data analytics to streamline and enhance the identification of human rights risks. Utilize advanced analytics tools to analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and detect potential risks. Consider leveraging emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate data analysis and identify human rights risks more efficiently.
Integrate Human Rights Due Diligence
Integrate human rights due diligence into your procurement and supplier management processes. Develop robust policies and codes of conduct that explicitly address human rights issues. Implement supplier screening mechanisms and incorporate human rights clauses into contracts. Regularly monitor and evaluate supplier compliance with human rights standards, utilizing performance indicators and key metrics.
Collaborate and Share Best Practices
Collaborate with industry peers, suppliers, and stakeholders to share best practices and knowledge. Engage in industry initiatives and partnerships aimed at promoting responsible supply chain practices. Participate in multi-stakeholder initiatives that focus on addressing human rights risks collectively. By sharing experiences and insights, companies can collectively enhance their ability to identify and mitigate human rights risks.
Key Challenges To Identifying Human Rights Risks in Your Supply Chain
Identifying human rights risks in your supply chain can pose various challenges. Some of the key challenges include:
Lack of Supply Chain Transparency
Limited visibility and transparency within complex supply chains make it difficult to trace the origin of raw materials and track their journey through various tiers of suppliers. This opacity makes it challenging to assess the human rights practices at each level and identify potential risks.
Limited Supplier Cooperation
Some suppliers may be reluctant to provide detailed information about their operations or may resist external assessments. They may fear reputational damage or potential disruptions to their business. This lack of cooperation makes it challenging to obtain accurate data and insights into human rights risks.
Global and Cultural Differences
Supply chains often span across different countries and cultures, each with its unique legal frameworks, labour practices, and cultural norms. Understanding and addressing human rights risks in diverse contexts can be complex, requiring cross-cultural sensitivity and expertise.
Subcontracting and Outsourcing
Subcontracting and outsourcing practices further complicate the identification of human rights risks. Companies may have limited visibility and control over subcontractors or sub-tier suppliers, making it challenging to assess the working conditions and human rights practices at these levels.
Inadequate Data and Information
Access to reliable and comprehensive data on suppliers’ labour practices and human rights performance can be limited. Supplier-provided information may not always be accurate or verifiable, making it difficult to assess risks accurately. Additionally, data gaps or inconsistencies can hinder effective risk analysis.
Constantly Evolving Risks
Human rights risks are not static and can evolve over time. New risks may emerge due to changes in local regulations, political environments, or social contexts. Staying updated and continuously monitoring these evolving risks requires dedicated resources and ongoing due diligence.
Resource Constraints
Conducting comprehensive assessments of human rights risks in the supply chain requires significant resources, including financial, human, and technological capabilities. Small and medium-sized enterprises or companies with limited resources may face challenges in dedicating the necessary resources for thorough risk identification.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive and multi-faceted approach. It involves engaging suppliers, leveraging technology and data analytics, collaborating with stakeholders, and adopting robust due diligence processes. Overcoming these challenges is crucial to creating more transparent, responsible, and sustainable supply chains that respect human rights.
The Role of AI In Identifying Human Rights Risks in Your Supply Chain
At Permutable, we know that AI plays a pivotal role in identifying human rights risks in supply chains by augmenting traditional approaches and providing advanced capabilities. Here are some ways AI can contribute:
Data Analysis and Pattern Recognition
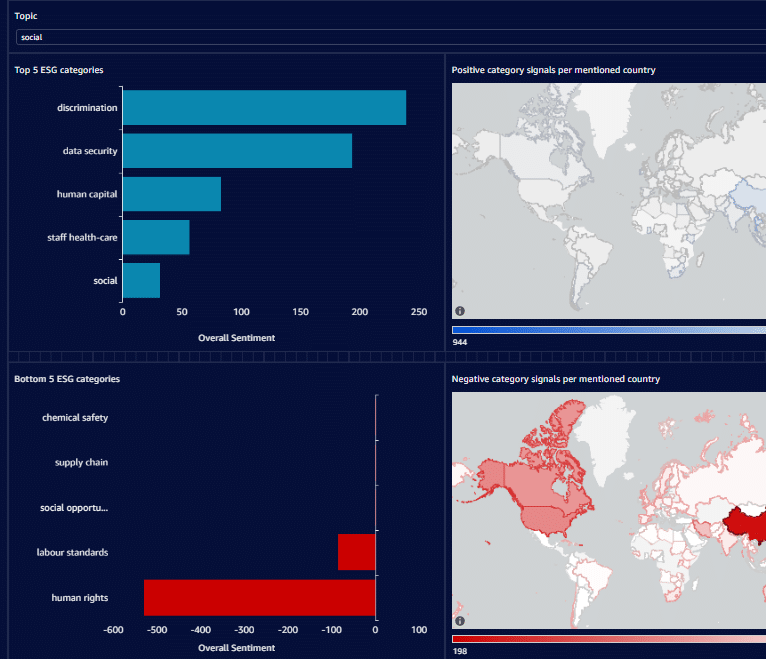
AI-powered algorithms can analyze large volumes of data from diverse sources, including supplier data, audits, news articles, and social media, to identify patterns and anomalies. By detecting indicators of potential human rights risks, AI enables more efficient and accurate risk assessment. At Permutable we use real-time monitoring to detect human rights risks as they break in local news sources, enabling real-time tracking of human rights violations and geo-location tagging.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP techniques allow AI systems to understand and extract information from unstructured data, such as supplier contracts, policies, and worker feedback. This enables companies to identify specific clauses, keywords, or sentiments that may indicate human rights violations or risky practices.
Supply Chain Mapping and Visualization
AI can facilitate supply chain mapping by integrating and analyzing data from multiple sources, including supplier databases and public records. Visualizing the supply chain network and the relationships within helps identify high-risk areas, such as regions with weak labour protections or suppliers with a history of violations.
Real-time Monitoring and Alerts
AI-powered monitoring systems like those provided as part of our supply chain risk monitoring dashboard can continuously track supplier performance, worker feedback, and external factors impacting human rights risks. This enables timely detection of potential violations or emerging risks, triggering alerts for immediate action and mitigation.
Predictive Analytics
By leveraging historical data and machine learning techniques, AI can predict future human rights risks in the supply chain. This enables companies to proactively allocate resources, implement preventive measures, and address potential risks before they escalate.
Supplier Risk Scoring
AI can assist in developing supplier risk scoring models by considering various factors, including supplier performance, compliance history, and external risk indicators. This automated scoring system helps prioritize suppliers for further assessment and focuses resources on high-risk areas.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
AI platforms can facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing among companies, industry associations, and other stakeholders. By pooling anonymized data and insights, AI systems can identify common human rights risks across industries and enable collective efforts to address these challenges.
While AI offers immense potential, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on, and biases or data gaps can affect the accuracy of risk identification. Human expertise and ethical considerations should complement AI systems to ensure responsible and accountable decision-making.
By harnessing the power of AI, companies can enhance their ability to proactively identify human rights risks in the supply chain, prioritize actions, and drive positive change. This technology enables more efficient and effective risk management, paving the way for responsible sourcing practices and the protection of human rights throughout global supply chains.
Conclusion
Identifying human rights risks in the supply chain is a vital step towards building an ethical and sustainable business. By understanding the scope of human rights risks, mapping the supply chain, conducting risk assessments, engaging with stakeholders, leveraging technology, and integrating due diligence, companies can gain valuable insights into potential risks. This enables proactive and targeted actions to mitigate human rights risks, protect workers, and foster a responsible and resilient supply chain. Embracing a holistic approach and collaborating with stakeholders will not only enhance the reputation and credibility of companies but also contribute to a more equitable and just global economy.
Find Out More
Discover the power of Permutable’s real-time supply chain risk monitoring solution in identifying human rights risks within your supply chain. Our cutting-edge technology combines AI, data analytics, and continuous monitoring to provide unparalleled insights into your supply chain operations. With our supply chain risk monitoring capabilities, you can proactively identify and address potential human rights risks, ensuring responsible and ethical practices throughout your supply chain.
Take action today and get in touch with our team to learn more about how Permutable’s solution can help your organization navigate the complex landscape of supply chain risk management. Our experts will guide you through a personalized demonstration, showcasing the capabilities of our platform in identifying and mitigating human rights risks. Together, we can foster transparency, promote ethical sourcing, and safeguard human rights within your supply chain.
Don’t let human rights risks go unnoticed. Contact us now and take a crucial step towards building a responsible and sustainable supply chain that aligns with your values and meets global standards.
