This sample report provides a comprehensive analysis of Tesco‘s supply chain network and its strategic relationships. It elucidates the supermarket giant’s interaction with various suppliers, the impact of high-profile corporate transactions, and the implications of key strategic decisions. The findings offer valuable insights into Tesco’s operational efficiency, market consolidation, talent management, and asset optimisation. The analysis concludes with recommendations for investors, competitors, suppliers, and partners.
Introduction
Tesco PLC is a British multinational groceries and general merchandise retailer with a global presence. As one of the market leaders, Tesco’s supply chain relationships and strategic decisions are critical to its success. This report critically assesses these relationships, drawing upon recent transactions and strategic developments.
Methodology
This report has been compiled using an advanced version of Permutable AI’s proprietary Supply Chain Network Analysis tool offering real-time feeds and comprehensive data windows into supplier and customer relationships. The analysis aims to understand the implications of Tesco’s actions on its market position, operational efficiency, and stakeholder relationships during the period 2020 – 2023.
Tesco’s supplier and customer networks were mapped out to identify first and second-tier relationships, using an analytical tool capable of scanning data across 50,000 websites, with a dataset encompassing 200,000 companies using advanced machine learning techniques.
High-profile corporate transactions were scrutinised, including divestitures and acquisitions, to assess their strategic significance and impact on Tesco’s market presence. Data on strategic moves by competitors were analysed to understand the competitive landscape and potential strategic responses by Tesco.
Potential risks within Tesco’s supply chain were identified and analysed, including threats from market volatility, regulatory changes, and competitive actions. Additionally, M&A due diligence practices were reviewed to ensure comprehensive understanding of Tesco’s strategic consolidation efforts.
Relationships with categorised based on suppliers, critics, regulators, market analysts, and plaintiffs. The data used in this report is limited to publicly available information and insights gained from primary sources. The analysis is based on the state of the market and Tesco’s operations during the period 2020 – 2023. Any significant changes post-publication may affect the report’s conclusions and recommendations.
The methodology adopted for this report ensures a thorough and nuanced understanding of Tesco’s supply chain dynamics and strategic positioning. By leveraging cutting-edge analytical tools, the report offers a detailed assessment, ensuring the findings are robust, reliable, and relevant to a wide range of stakeholders.
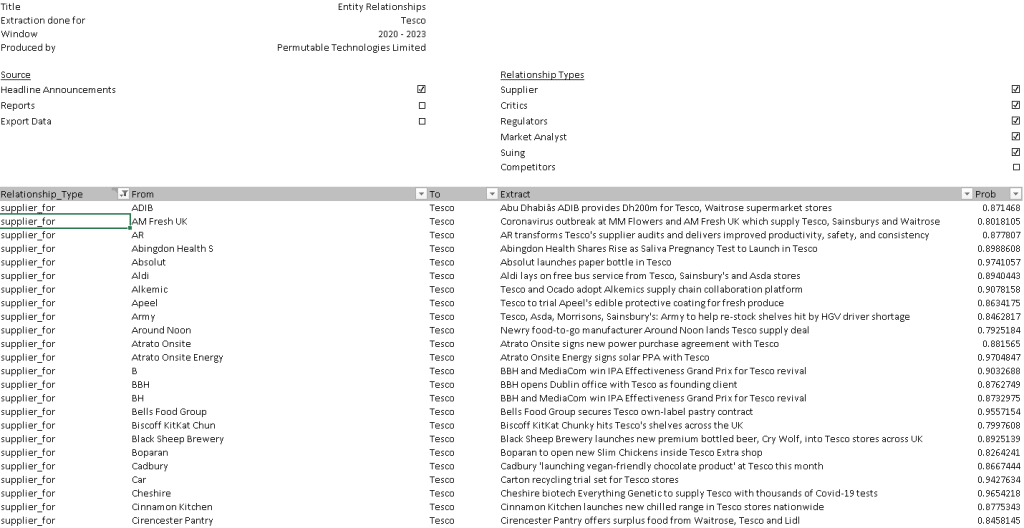
Above: Tesco supply chain relationship links data snippet
Key findings
Analysis
1. Tesco’s strategic divestment and market focus
A pivotal aspect of Tesco’s strategy has been the divestment of its business in Thailand and Malaysia to the CP Group. Finalised in 2021, this decision marked Tesco’s commitment to concentrate on its UK and European markets. By exiting these Asian markets, Tesco aimed to reduce operational complexity and the associated risks of local market competition and regulatory environments. The move was designed to strengthen its balance sheet and refocus resources on areas with a higher return on investment, demonstrating a clear strategy of market prioritisation and capital allocation efficiency.
2. Capital and operational efficiency
The sale of Tesco Bank’s mortgage portfolio to Lloyds Banking Group for approximately £3.8 billion underscores Tesco’s initiative to streamline its operations. The transaction involved the transfer of around 23,000 customers and was part of Tesco’s broader strategy to exit non-core banking operations. This shift enables Tesco to redirect its focus towards its primary retail business, which aligns with its aim of achieving capital efficiency and enhancing shareholder value.
3. Talent acquisition and retention
The retail sector is known for its competitive nature, particularly in the pursuit of top talent. Marks & Spencer’s acquisition of a high-ranking executive from Tesco signifies the intense competition for key personnel. This loss necessitates that Tesco reassess its approach to talent retention, ensuring that it can maintain a leadership team capable of propelling future growth and maintaining its market-leading position.
4. Asset liquidation for reinvestment
Tesco’s strategy of liquidating non-essential real estate assets is evidenced by the selling off of non-core properties, including undeveloped land, old stores that have been closed, and other properties not central to its core grocery business. This has included selling off parcels of land that were originally acquired for expansion but were deemed surplus to requirements. This strategy reflects Tesco’s aim to generate capital for reinvestment into more critical areas such as store technology and customer service. Such decisions highlight the company’s intent to enhance its retail operations and improve overall customer satisfaction.
5. Optimisation of store network
The acquisition of several Tesco stores in Eastern Europe by Kaufland, following regulatory approval, suggests a conscious effort by Tesco to optimise its store network. This may be part of Tesco’s strategy to withdraw from underperforming markets, thereby allowing the company to focus on areas with better profitability and to channel investments towards growing its online sales.
Implications and strategic moves
Tesco’s portfolio of transactions and the consequential reshaping of its supply chain are not just tactical adjustments but signal a strategic realignment with far-reaching implications. The company has shown a clear preference for optimising operations, both in its retail offerings and in its back-end supply chain management. The following are the expanded implications and strategic moves identified from Tesco’s recent activities:
1. Streamlining for focus
The divestment of its businesses in Thailand and Malaysia not only allowed Tesco to enhance its capital efficiency but also indicated a strategic focus on markets where the company holds a comparative advantage. This concentration on the UK and European markets suggests a strategic move away from diversification and towards specialisation, allowing for a more targeted and potentially more effective management of resources.
2. Technological integration
By liquidating non-essential real estate and investing in store technology, Tesco is positioning itself at the forefront of retail innovation. The investments in customer service technologies could offer a dual benefit of enhancing the customer experience and streamlining operational processes. The introduction of new technologies into Tesco’s supply chain could lead to more sophisticated data analytics, better inventory management, and a more personalised shopping experience for customers.
3. Responsive market strategy
The sale of Eastern European stores to Kaufland reflects Tesco’s agility in responding to market signals. This retreat from less profitable areas to focus on core markets demonstrates a responsiveness that could allow Tesco to dynamically adapt to changing consumer trends and economic climates.
4. Online and physical synergy
The strategic consolidation of physical stores, coupled with investments towards online sales growth, hints at Tesco’s vision of creating a harmonious synergy between brick-and-mortar locations and e-commerce. The company is realising the potential of omnichannel retailing, where the interaction between physical and online offerings is seamless, and where each channel supports and enhances the other.
5. Supply chain resilience
Tesco’s strategic decisions have implications for the robustness of its supply chain. By streamlining its supplier relationships and focusing on technological advancements, the company is likely to enhance its supply chain resilience, allowing for better risk management and response to disruptions.
6. Talent dynamics
The poaching of a high-ranking Tesco executive by Marks & Spencer is a poignant reminder of the competitive nature of the retail sector. Tesco’s response to this will be a key determinant of its future success. Investing in talent development and creating a robust succession plan will be imperative for Tesco to sustain its market leadership.
7. Stakeholder engagement
All these strategic moves suggest a need for heightened stakeholder engagement. By keeping open channels of communication with suppliers, investors, and employees, Tesco can ensure that its strategic realignment is understood and supported across its operational ecosystem.
The analysis of these implications shows that Tesco’s strategic moves are both a reflection of its current priorities and an indication of its future trajectory. Each decision carries weight for how the company is viewed by its stakeholders, how it is positioned in the market, and how it can weather the challenges of a rapidly evolving retail landscape.
The agility with which Tesco has approached its strategic overhaul is indicative of a larger trend in the retail industry towards adaptability and customer-centrism. As Tesco continues to refine its operations and enhance its supply chain, it sets a benchmark for other retailers to follow, signifying a transformative phase in retail management where efficiency, innovation, and strategic foresight become key drivers of success.
Recommendations for stakeholders
1. Investors
Investors should interpret Tesco’s strategic divestitures as a realignment towards strengthening core business areas, which is expected to streamline operations and is expected to contribute towards continued favourable financial performance.
2. Competitors
Competitors have the opportunity to learn from Tesco’s strategic shifts and can potentially capitalise on market segments Tesco has exited. This information can be used to enhance their strategic positioning within the retail industry.
3. Suppliers and partners
Suppliers and partners must stay adaptable to Tesco’s evolving business needs. There may be changes in demand, necessitating agility in supply chain operations to maintain a seamless partnership with Tesco.
Tesco’s supply chain network: Conclusion
Tesco’s strategic decisions and supply chain relationships indicate a concerted effort to prioritise efficiency, focus on profitable markets, and leverage technological advancements. The company’s ability to restructure its operations, manage its asset portfolio effectively, and adapt to a changing market is indicative of its resilient business model. The various strategic moves, from talent management to real estate optimisation, reflect a forward-thinking approach designed to position Tesco for future success.
As Tesco continues to adapt to the fast-evolving retail landscape, its supply chain strategies and relationship management remain pivotal. With careful monitoring and analysis, stakeholders can anticipate the company’s future direction and make informed decisions.
Find out more
For further information or to explore additional insights, you may wish to consider the following options:
Purchase of original dataset: To acquire the original data set upon which this report is based, please contact us directly. This will provide you with the comprehensive raw data, enabling deeper analysis and customisation to meet your specific needs.
Request custom reports: If you require analytical insights on another company or a different sector, we are available to compile tailored reports. These can be customised to focus on specific areas of interest or to address particular questions you may have.
To proceed with either option, or if you have any other enquiries, please reach out to us via email at enquiries@permutable.ai. We are here to assist you with your data and analytical needs, and we look forward to your correspondence.
Further reading
Found this article useful? Why not read more supply chain insights from us on:
Coca-Cola supply chain sustainability
Unilever supply chain sustainability
Tesco’s supply chain network and strategic relationships