Corporate sustainability has become an integral part of business operations, with companies competing to demonstrate their commitment to environmental, social, and governance criteria. Amazon, the global e-commerce giant, is no exception. With its vast operations and increasing market influence, understanding the Amazon ESG score is essential.
In this article, we take a deep dive into the factors that contribute to the Amazon ESG score according to our data and uncover the key to its corporate sustainability. By analyzing Amazon’s environmental initiatives, social impact endeavours, and governance practices, we shed light on how the company manages its ESG responsibilities.
Understanding Amazon’s ESG score and its importance
ESG is a set of criteria that investors, customers, and other stakeholders use to evaluate the sustainability and ethical impact of a company’s operations. Our Amazon ESG score is a measure of how the company performs in these areas based on sentiment analysis. It is essential because it affects the company’s reputation, financial performance, and ability to attract and retain customers and investors.
Our Amazon ESG score is based on its performance in three areas: environmental sustainability, social sustainability, and governance. Environmental sustainability focuses on reducing the company’s impact on the environment, while social sustainability focuses on improving the well-being of employees, customers, and communities. Governance covers how the company is managed, ensuring transparency and accountability.

Factors contributing to Amazon’s ESG score
Our Amazon ESG score is influenced by various factors, including its environmental, social, and governance practices.
Environmental sustainability initiatives at Amazon
Amazon has implemented various measures to reduce its carbon footprint and improve the sustainability of its operations. The company has committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2040 and has invested heavily in renewable energy sources. It has also launched initiatives such as the Climate Pledge, which encourages other companies to commit to reducing their carbon footprint.
In addition to its efforts to reduce carbon emissions, Amazon has implemented sustainable packaging initiatives. The company has introduced Frustration-Free Packaging, which uses less material and is easier to open, reducing waste. Amazon has also pledged to make all of its packaging recyclable by 2025.
However there is still plenty of room for improvement as their score of 72 in environmental factors implies.
Amazon produces a significant amount of packaging waste, much of which is not recyclable. In 2020, Amazon generated over 600 million pounds of plastic packaging waste in the United States alone. Their massive transportation network is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. The company has a fleet of over 100,000 delivery vehicles, and it also ships products by air and sea.
In addition, their data centers and warehouses consume a large amount of energy. In 2020, Amazon’s energy consumption was equivalent to the annual electricity consumption of over 1 million homes, while their operations require a significant amount of water, particularly for its data centers and fulfillment centers. In 2020, Amazon withdrew over 100 billion gallons of water from the environment.
In addition to these specific issues, Amazon has also been criticized for its overall environmental impact. Many critics have argued that Amazon’s business model, which encourages consumers to buy more and more goods, is unsustainable in the long term.
Social sustainability initiatives at Amazon
Amazon’s ESG score according to our sentiment data comes in at a sub par 42. This will be of no surprise to those who have been following criticism of its poor worker safety record. In 2021, the company’s injury rate was nearly double the industry average. Amazon has also been accused of failing to provide its workers with adequate breaks and of retaliating against workers who speak out about safety concerns.
Amazon has also been criticized for its unfair labour practices. The company has been accused of suppressing unionization efforts and of paying its workers low wages. Amazon has also been accused of firing workers for minor infractions and of denying workers bathroom breaks. Amazon’s track record in regards to diversity and inclusion has also come under fire. The company’s workforce is predominantly white and male, and its leadership team is even less diverse. Amazon has also been accused of discriminating against women and minorities in hiring and promotion.
In addition to these specific issues, Amazon has also been criticized for its overall social impact. For example, some critics have argued that Amazon’s business model, which relies on low-cost labour and aggressive competition, is harmful to workers and communities.
Amazon is aware of its social impact and has taken steps to improve its social performance. For example, the company has raised its minimum wage and has pledged to invest in worker safety. Amazon has also launched a number of diversity and inclusion initiatives. However, the company still has a long way to go to improve its social ESG score.
Governance practices at Amazon
Amazon’s governance score is low at 23. This is due to a variety of reasons including a lack of independent board members (Amazon’s board of directors is dominated by insiders and allies of CEO Andy Jassy) raising concerns about the company’s accountability and transparency. Meanwhile, Amazon’s shareholders have limited rights, such as the right to nominate directors and to vote on executive compensation. This makes it difficult for shareholders to hold management accountable.
Amazon’s executive compensation is excessive, particularly given the company’s poor social and environmental performance while the company spends heavily on lobbying and campaign contributions, raising concerns about the company’s influence on government policy.
In addition to these specific issues, Amazon has also been criticized for its overall governance practices. For example, some critics have argued that Amazon’s culture of secrecy and its focus on short-term profits make it difficult for the company to make responsible long-term decisions.
Although some improvements have been made in this area such as the addition of some independent board members and increased shareholders rights, the company still has a long way to go to improve its governance ESG score.
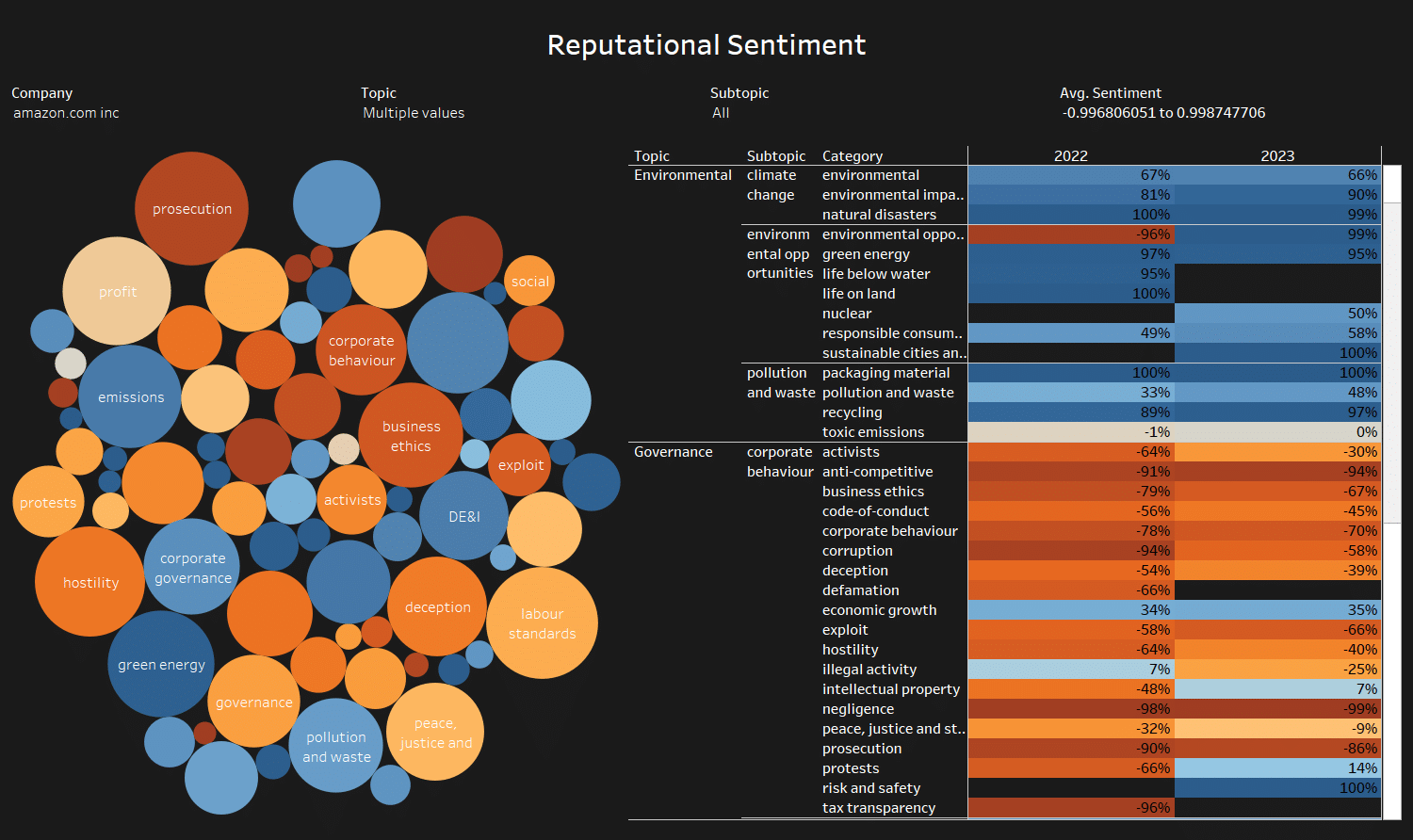
The impact of Amazon’s ESG score on its reputation and stakeholders
Amazon’s ESG score has a significant impact on its reputation and stakeholders. A high ESG score can improve the company’s reputation, attracting customers and investors who prioritize sustainability and ethical business practices. A low ESG score can damage the company’s reputation, leading to decreased trust from customers and investors.
Moreover, Amazon’s ESG score can impact its relationships with stakeholders, including employees, suppliers, and local communities. A strong ESG score can improve the company’s relationships with stakeholders, leading to increased loyalty and support.
Comparing Amazon’s ESG score with other companies in the industry
Comparing Amazon’s ESG score with other companies in the industry provides insights into how it performs in terms of sustainability and ethical business practices. According to the 2021 Corporate Knights Global 100 Most Sustainable Corporations, Amazon ranked 92nd, with a weighted ESG score of 51.4%.
See our ESG scores for Amazon’s competitors to see how they compare:
While Amazon’s ESG score is lower than some of its competitors, such as Microsoft and Alphabet, the company has made significant progress in recent years. By investing in renewable energy, reducing waste, and promoting diversity and inclusion, Amazon is paving the way for a more sustainable future in the corporate world.
Challenges and criticisms of Amazon’s sustainability efforts
Amazon’s sustainability efforts have faced criticism from various stakeholders. Some environmental activists argue that the company’s carbon reduction targets are not ambitious enough, and that it should do more to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. Others criticize Amazon’s labor practices, including low wages and poor working conditions in its warehouses.
Despite these criticisms, Amazon has taken steps to address these issues. The company has pledged to invest in renewable energy and improve working conditions for its employees. However, there is still room for improvement, and Amazon must continue to address these challenges to improve its ESG score and maintain its reputation as a sustainable and ethical company.
Conclusion: The future of corporate sustainability and the role of ESG scores
Corporate sustainability and ESG scores will continue to play an essential role in the business world. Companies that prioritize sustainability and ethical business practices will have a competitive advantage, attracting customers and investors who prioritize these values.
By understanding Amazon’s ESG score and the factors that contribute to it, we can gain insights into how the company manages its ESG responsibilities. Amazon’s commitment to environmental sustainability, social impact, and governance practices demonstrates its dedication to corporate sustainability. By continuing to invest in renewable energy, reduce waste, and promote diversity and inclusion, Amazon is setting an example for other companies to follow.
As consumers and investors increasingly prioritize sustainability and ethical business practices, ESG scores will become even more critical. Companies must prioritize sustainability and transparency to succeed in the future of the business world.
Find out more
Are you looking for more granular data on Amazon’s ESG practices?
