Unilever, the British-Dutch multinational consumer goods company that produces and sells a wide range of products, including food, beverages, cleaning agents, and personal care products has a significant impact on the environment and society with operations in over 190 countries and a workforce of more than 155,000 people. In recent years, Unilever has made significant efforts to reduce its environmental footprint and promote social responsibility. Our ESG data shows that the Unilever ESG score is impressive, and in this article, we’ll take a closer look at Unilever’s sustainability initiatives, including its pledge to achieve net-zero emissions by 2039, its efforts to reduce plastic waste, and its commitment to promoting sustainable agriculture.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding ESG scores
ESG scores are a measure of a company’s performance in areas related to sustainability and corporate responsibility. The score assesses a company’s impact on the environment, its social practices, and its governance structure. The score is based on a range of factors, including a company’s greenhouse gas emissions, energy use, water consumption, waste management, labour practices, human rights, diversity, and board structure.
A high ESG score indicates that a company is taking significant steps to reduce its environmental impact, promote social responsibility, and ensure good governance. The score is increasingly important for investors, who are looking to invest in companies that are committed to sustainability and responsible business practices. In recent years, there has been a growing trend of investors prioritizing ESG factors when making investment decisions.
Unilever ESG score: How it compares to its competitors
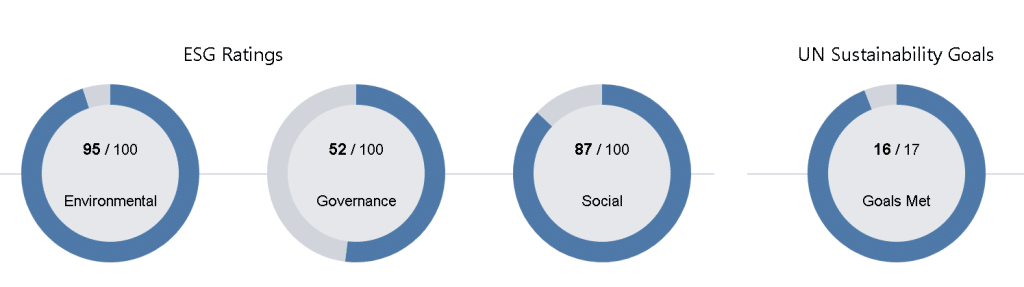
Unilever has been making significant efforts to reduce its environmental impact and promote social responsibility, earning an impressive ESG score. According to our ESG data, they score 95 in environment, 87 in social, and 52 in governance placing it in the 99th percentile of companies in its industry.
The Unilever ESG score is just higher than its competitors in the consumer goods industry, including Procter & Gamble and Nestle. The company’s environmental practices, including its efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable agriculture, are particularly strong. Unilever is also committed to social responsibility, including promoting diversity and inclusion, ensuring fair labour practices, and supporting community development.
Take a closer look additional peer ESG scores below:
Unilever’s sustainable sourcing practices
Unilever is committed to sourcing its raw materials sustainably, including palm oil, soy, and tea. The company has set a target to source 100% of its agricultural raw materials sustainably by 2023. Unilever’s sustainable sourcing practices include working with suppliers to promote sustainable farming practices, reducing deforestation, and protecting biodiversity.
One of Unilever’s flagship sustainable sourcing programs is the Sustainable Agriculture Code, which sets out a series of principles and practices for sustainable farming. The program covers a wide range of issues, including soil health, water conservation, biodiversity, and fair labour practices. Unilever has also signed the Cerrado Manifesto, a commitment to protect Brazil’s Cerrado region, one of the world’s most biodiverse savannas.
Unilever’s waste reduction efforts
Unilever is committed to reducing waste throughout its operations, including its factories, offices, and supply chain. The company has set a target to halve its use of virgin plastic by 2025 and to ensure that all of its plastic packaging is reusable, recyclable, or compostable by 2025.
To achieve these goals, Unilever is investing in new packaging technologies, promoting recycling, and reducing the amount of plastic used in its products. The company has also launched several initiatives to encourage consumers to reduce their plastic waste, including refillable packaging and reusable containers.
Unilever’s greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets
Unilever is committed to reducing its greenhouse gas emissions throughout its operations, including its factories, offices, and supply chain. The company has set a target to achieve net-zero emissions from its products by 2039, including the emissions generated by the use of its products by consumers.
To achieve this goal, Unilever is investing in renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and reducing the carbon footprint of its supply chain. The company has also launched several initiatives to promote sustainable living, including the “Clean Future” program, which aims to replace fossil fuels with renewable and recycled carbon sources in its cleaning and laundry products.
Unilever’s social impact initiatives
Unilever is committed to promoting social responsibility and supporting community development. The company set a target to improve the livelihoods of 1 million people in its value chain by 2020 and has exceeded this target.
Unilever is also committed to promoting diversity and inclusion, ensuring fair labour practices, and promoting human rights. The company has launched several initiatives to support these goals, including the “Unstereotype Alliance,” which aims to eliminate stereotypes in advertising, and the “Fairness in the Workplace” program, which promotes fair labour practices in its operations and supply chain.
Unilever’s involvement in sustainable packaging
Unilever is committed to promoting sustainable packaging and reducing its use of plastic. The company has set a target to ensure that all of its plastic packaging is reusable, recyclable, or compostable by 2025 and to halve its use of virgin plastic by the same year.
To achieve these goals, Unilever is investing in new packaging technologies, promoting recycling, and reducing the amount of plastic used in its products. The company has also launched several initiatives to encourage consumers to reduce their plastic waste, including refillable packaging and reusable containers.
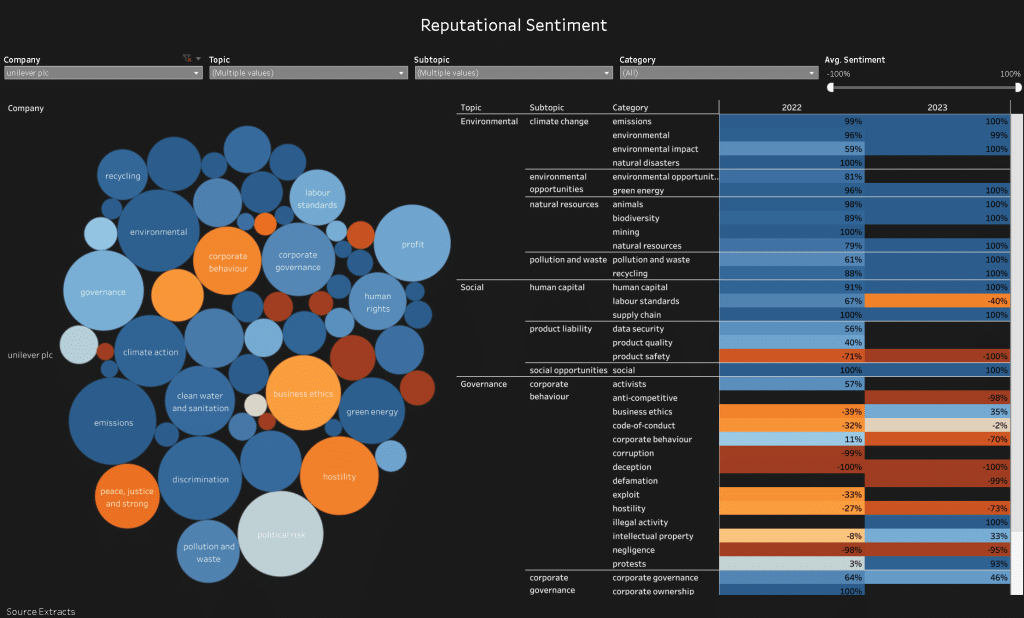
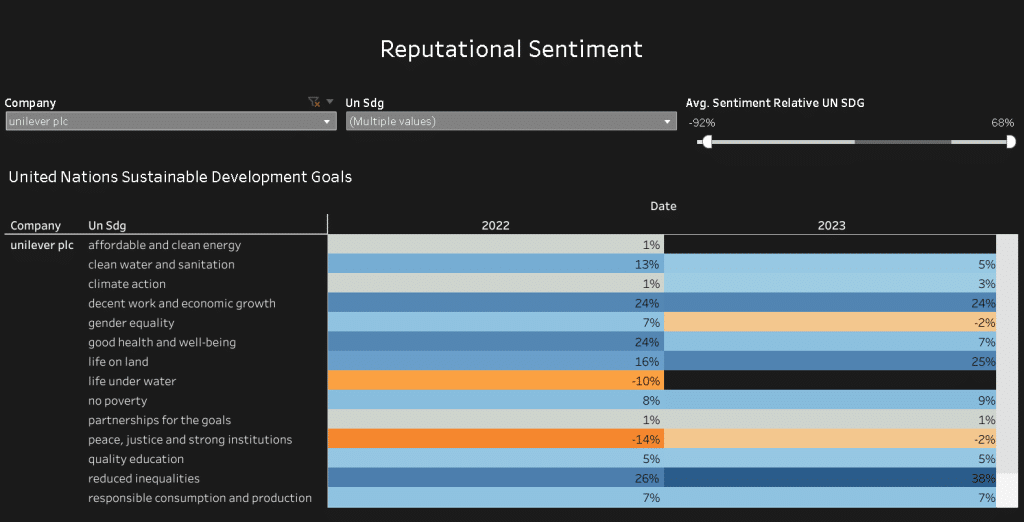
Criticisms of Unilever’s sustainability efforts
Despite Unilever’s impressive sustainability initiatives, the company has faced criticism from some environmental and social justice groups. Some critics argue that the company’s commitments are not ambitious enough, particularly in the areas of greenhouse gas emissions reduction and plastic waste reduction. Others argue that the company’s sustainability initiatives are too focused on corporate responsibility and not enough on systemic change.
The company has also faced accusations of greenwashing in recent years. While Unilever has been recognized for its sustainability commitments and efforts, some critics have raised concerns about specific products, claims, or practices that they perceive as greenwashing. It is important to note that accusations of greenwashing can vary and may be subject to differing perspectives and interpretations.
Unilever has also taken steps to address these concerns and improve transparency in their sustainability reporting. They have made commitments to reduce environmental impact, promote responsible sourcing, and increase social and economic inclusion. Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan outlines their goals and initiatives in various areas, including climate change, waste reduction, and social impact.
As with any company, it is advisable to conduct independent research and consider multiple sources to form a comprehensive understanding of their sustainability practices and their alignment with stated commitments.
Unilever’s governance score
Unilever’s relatively low governance score of 52 can be attributed to several significant factors, each bearing implications for the company’s corporate governance practices. One notable concern revolves around Unilever’s board of directors, which has faced criticism for its lack of independence. A substantial proportion of the board comprises executive directors, individuals who are concurrently employed by the company. This dual role raises questions regarding the board’s ability to provide impartial oversight of management decisions.
The effectiveness of Unilever’s audit committee has also come under scrutiny. Critics have highlighted concerns about the committee’s transparency and its degree of independence from the company’s management, raising issues about the thoroughness of financial oversight. Specifically, Unilever has faced criticism for its limited transparency and disclosure related to its corporate governance practices. Stakeholders have expressed concerns about insufficient information provided to shareholders regarding board composition and executive compensation practices.
Unilever’s dual-class share structure has faced criticism for its potential to disenfranchise minority shareholders. The company’s founders and insiders hold a greater share of voting power compared to other shareholders, resulting in limited influence for minority shareholders on corporate decisions. Furthermore, Unilever’s executive compensation practices have been a point of contention, with concerns about their perceived excessiveness and their alignment with shareholder interests. Notably, the company’s CEO has been among the highest-paid CEOs in the UK, a position that contrasts with the company’s relatively lackluster financial performance in recent years.
Addressing these areas of concern may pave the way for Unilever to improve its governance practices and bolster its overall governance score, aligning the company’s operations more closely with the interests of all its stakeholders.
2024 update: Unilever’s commitment to sustainable business
As Unilever continues to navigate the complexities of the global market in 2024, the company remains steadfast in its commitment to sustainable business practices. Under the leadership of CEO Hein Schumacher, Unilever has made significant strides in enhancing its sustainability performance, reinforcing its position as a leader in corporate responsibility within the consumer goods industry.
Sustainability performance highlights
Unilever’s sustainability efforts are guided by its long-term vision to create a positive impact on both the environment and society. The company’s pledge to achieve net-zero emissions by 2039 reflects its dedication to addressing climate and nature challenges. This ambitious goal is supported by substantial investments in renewable energy, sustainable sourcing, and innovative product development aimed at reducing the carbon footprint of its operations and supply chain.
Key initiatives in 2024
-
Sustainable agriculture and waste reduction: Unilever continues to prioritize sustainable sourcing of raw materials, including palm oil, soy, and tea. The company’s Sustainable Agriculture Code and its commitment to the Cerrado Manifesto are central to these efforts. Additionally, Unilever is making progress toward its target of halving the use of virgin plastic by 2025, with several initiatives aimed at promoting reusable, recyclable, or compostable packaging.
-
Leadership in climate action: Under Hein Schumacher’s leadership, Unilever is focused on driving systemic change in its approach to climate and nature. The company’s “Clean Future” program, which seeks to replace fossil fuels with renewable and recycled carbon sources in its cleaning and laundry products, exemplifies its commitment to sustainability.
Final thoughts: Unilever ESG score and sustainability commitments
Unilever’s commitment to sustainability and net zero has earned it an impressive ESG score, placing it at the forefront of corporate responsibility in the consumer goods industry. The company’s sustainability and social impact initiatives are significant steps toward a more sustainable future. While Unilever’s sustainability efforts are not without criticism, the company’s commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices is a positive sign for the future of corporate responsibility.
Ready to dive deeper into the data behind Unilever’s ESG performance? Unlock the potential for more granular insights on Unilever by reaching out to Permutable AI. Contact us at enquiries@permutable.ai or simply complete the form below. Let’s explore the finer details together.
Get in touch
Are you looking for more granular data on Unilever’s ESG practices?
